Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What is a Research Hypothesis: How to Write it, Types, and Examples

Any research begins with a research question and a research hypothesis . A research question alone may not suffice to design the experiment(s) needed to answer it. A hypothesis is central to the scientific method. But what is a hypothesis ? A hypothesis is a testable statement that proposes a possible explanation to a phenomenon, and it may include a prediction. Next, you may ask what is a research hypothesis ? Simply put, a research hypothesis is a prediction or educated guess about the relationship between the variables that you want to investigate.
It is important to be thorough when developing your research hypothesis. Shortcomings in the framing of a hypothesis can affect the study design and the results. A better understanding of the research hypothesis definition and characteristics of a good hypothesis will make it easier for you to develop your own hypothesis for your research. Let’s dive in to know more about the types of research hypothesis , how to write a research hypothesis , and some research hypothesis examples .
Table of Contents
What is a hypothesis ?
A hypothesis is based on the existing body of knowledge in a study area. Framed before the data are collected, a hypothesis states the tentative relationship between independent and dependent variables, along with a prediction of the outcome.
What is a research hypothesis ?
Young researchers starting out their journey are usually brimming with questions like “ What is a hypothesis ?” “ What is a research hypothesis ?” “How can I write a good research hypothesis ?”
A research hypothesis is a statement that proposes a possible explanation for an observable phenomenon or pattern. It guides the direction of a study and predicts the outcome of the investigation. A research hypothesis is testable, i.e., it can be supported or disproven through experimentation or observation.
Characteristics of a good hypothesis
Here are the characteristics of a good hypothesis :
- Clearly formulated and free of language errors and ambiguity
- Concise and not unnecessarily verbose
- Has clearly defined variables
- Testable and stated in a way that allows for it to be disproven
- Can be tested using a research design that is feasible, ethical, and practical
- Specific and relevant to the research problem
- Rooted in a thorough literature search
- Can generate new knowledge or understanding.
How to create an effective research hypothesis
A study begins with the formulation of a research question. A researcher then performs background research. This background information forms the basis for building a good research hypothesis . The researcher then performs experiments, collects, and analyzes the data, interprets the findings, and ultimately, determines if the findings support or negate the original hypothesis.
Let’s look at each step for creating an effective, testable, and good research hypothesis :
- Identify a research problem or question: Start by identifying a specific research problem.
- Review the literature: Conduct an in-depth review of the existing literature related to the research problem to grasp the current knowledge and gaps in the field.
- Formulate a clear and testable hypothesis : Based on the research question, use existing knowledge to form a clear and testable hypothesis . The hypothesis should state a predicted relationship between two or more variables that can be measured and manipulated. Improve the original draft till it is clear and meaningful.
- State the null hypothesis: The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between the variables you are studying.
- Define the population and sample: Clearly define the population you are studying and the sample you will be using for your research.
- Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis: Select appropriate research methods, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies, which will allow you to test your research hypothesis .
Remember that creating a research hypothesis is an iterative process, i.e., you might have to revise it based on the data you collect. You may need to test and reject several hypotheses before answering the research problem.
How to write a research hypothesis
When you start writing a research hypothesis , you use an “if–then” statement format, which states the predicted relationship between two or more variables. Clearly identify the independent variables (the variables being changed) and the dependent variables (the variables being measured), as well as the population you are studying. Review and revise your hypothesis as needed.
An example of a research hypothesis in this format is as follows:
“ If [athletes] follow [cold water showers daily], then their [endurance] increases.”
Population: athletes
Independent variable: daily cold water showers
Dependent variable: endurance
You may have understood the characteristics of a good hypothesis . But note that a research hypothesis is not always confirmed; a researcher should be prepared to accept or reject the hypothesis based on the study findings.

Research hypothesis checklist
Following from above, here is a 10-point checklist for a good research hypothesis :
- Testable: A research hypothesis should be able to be tested via experimentation or observation.
- Specific: A research hypothesis should clearly state the relationship between the variables being studied.
- Based on prior research: A research hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and previous research in the field.
- Falsifiable: A research hypothesis should be able to be disproven through testing.
- Clear and concise: A research hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner.
- Logical: A research hypothesis should be logical and consistent with current understanding of the subject.
- Relevant: A research hypothesis should be relevant to the research question and objectives.
- Feasible: A research hypothesis should be feasible to test within the scope of the study.
- Reflects the population: A research hypothesis should consider the population or sample being studied.
- Uncomplicated: A good research hypothesis is written in a way that is easy for the target audience to understand.
By following this research hypothesis checklist , you will be able to create a research hypothesis that is strong, well-constructed, and more likely to yield meaningful results.

Types of research hypothesis
Different types of research hypothesis are used in scientific research:
1. Null hypothesis:
A null hypothesis states that there is no change in the dependent variable due to changes to the independent variable. This means that the results are due to chance and are not significant. A null hypothesis is denoted as H0 and is stated as the opposite of what the alternative hypothesis states.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is not zoonotic .”
2. Alternative hypothesis:
This states that there is a significant difference or relationship between the variables being studied. It is denoted as H1 or Ha and is usually accepted or rejected in favor of the null hypothesis.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is zoonotic .”
3. Directional hypothesis :
This specifies the direction of the relationship or difference between variables; therefore, it tends to use terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: “ The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment .”
4. Non-directional hypothesis:
While it does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables, a non-directional hypothesis states the existence of a relationship or difference between variables but not the direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship. A non-directional hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or when findings contradict previous research.
Example, “ Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express .”
5. Simple hypothesis :
A simple hypothesis only predicts the relationship between one independent and another independent variable.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging .”
6 . Complex hypothesis :
A complex hypothesis states the relationship or difference between two or more independent and dependent variables.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging, reduces sun burn, and reduces the chances of skin cancer .” (Here, the three dependent variables are slowing skin aging, reducing sun burn, and reducing the chances of skin cancer.)
7. Associative hypothesis:
An associative hypothesis states that a change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables.
Example: “ There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health .”
8 . Causal hypothesis:
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect interaction between variables.
Example: “ Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage .”
Note that some of the types of research hypothesis mentioned above might overlap. The types of hypothesis chosen will depend on the research question and the objective of the study.

Research hypothesis examples
Here are some good research hypothesis examples :
“The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.”
“Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.”
“Plants that are exposed to certain types of music will grow taller than those that are not exposed to music.”
“The use of the plant growth regulator X will lead to an increase in the number of flowers produced by plants.”
Characteristics that make a research hypothesis weak are unclear variables, unoriginality, being too general or too vague, and being untestable. A weak hypothesis leads to weak research and improper methods.
Some bad research hypothesis examples (and the reasons why they are “bad”) are as follows:
“This study will show that treatment X is better than any other treatment . ” (This statement is not testable, too broad, and does not consider other treatments that may be effective.)
“This study will prove that this type of therapy is effective for all mental disorders . ” (This statement is too broad and not testable as mental disorders are complex and different disorders may respond differently to different types of therapy.)
“Plants can communicate with each other through telepathy . ” (This statement is not testable and lacks a scientific basis.)
Importance of testable hypothesis
If a research hypothesis is not testable, the results will not prove or disprove anything meaningful. The conclusions will be vague at best. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher focus on the study outcome and understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher make precise predictions based on prior research.
To be considered testable, there must be a way to prove that the hypothesis is true or false; further, the results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on research hypothesis
1. What is the difference between research question and research hypothesis ?
A research question defines the problem and helps outline the study objective(s). It is an open-ended statement that is exploratory or probing in nature. Therefore, it does not make predictions or assumptions. It helps a researcher identify what information to collect. A research hypothesis , however, is a specific, testable prediction about the relationship between variables. Accordingly, it guides the study design and data analysis approach.
2. When to reject null hypothesis ?
A null hypothesis should be rejected when the evidence from a statistical test shows that it is unlikely to be true. This happens when the test statistic (e.g., p -value) is less than the defined significance level (e.g., 0.05). Rejecting the null hypothesis does not necessarily mean that the alternative hypothesis is true; it simply means that the evidence found is not compatible with the null hypothesis.
3. How can I be sure my hypothesis is testable?
A testable hypothesis should be specific and measurable, and it should state a clear relationship between variables that can be tested with data. To ensure that your hypothesis is testable, consider the following:
- Clearly define the key variables in your hypothesis. You should be able to measure and manipulate these variables in a way that allows you to test the hypothesis.
- The hypothesis should predict a specific outcome or relationship between variables that can be measured or quantified.
- You should be able to collect the necessary data within the constraints of your study.
- It should be possible for other researchers to replicate your study, using the same methods and variables.
- Your hypothesis should be testable by using appropriate statistical analysis techniques, so you can draw conclusions, and make inferences about the population from the sample data.
- The hypothesis should be able to be disproven or rejected through the collection of data.
4. How do I revise my research hypothesis if my data does not support it?
If your data does not support your research hypothesis , you will need to revise it or develop a new one. You should examine your data carefully and identify any patterns or anomalies, re-examine your research question, and/or revisit your theory to look for any alternative explanations for your results. Based on your review of the data, literature, and theories, modify your research hypothesis to better align it with the results you obtained. Use your revised hypothesis to guide your research design and data collection. It is important to remain objective throughout the process.
5. I am performing exploratory research. Do I need to formulate a research hypothesis?
As opposed to “confirmatory” research, where a researcher has some idea about the relationship between the variables under investigation, exploratory research (or hypothesis-generating research) looks into a completely new topic about which limited information is available. Therefore, the researcher will not have any prior hypotheses. In such cases, a researcher will need to develop a post-hoc hypothesis. A post-hoc research hypothesis is generated after these results are known.
6. How is a research hypothesis different from a research question?
A research question is an inquiry about a specific topic or phenomenon, typically expressed as a question. It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis.
7. Can a research hypothesis change during the research process?
Yes, research hypotheses can change during the research process. As researchers collect and analyze data, new insights and information may emerge that require modification or refinement of the initial hypotheses. This can be due to unexpected findings, limitations in the original hypotheses, or the need to explore additional dimensions of the research topic. Flexibility is crucial in research, allowing for adaptation and adjustment of hypotheses to align with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
8. How many hypotheses should be included in a research study?
The number of research hypotheses in a research study varies depending on the nature and scope of the research. It is not necessary to have multiple hypotheses in every study. Some studies may have only one primary hypothesis, while others may have several related hypotheses. The number of hypotheses should be determined based on the research objectives, research questions, and the complexity of the research topic. It is important to ensure that the hypotheses are focused, testable, and directly related to the research aims.
9. Can research hypotheses be used in qualitative research?
Yes, research hypotheses can be used in qualitative research, although they are more commonly associated with quantitative research. In qualitative research, hypotheses may be formulated as tentative or exploratory statements that guide the investigation. Instead of testing hypotheses through statistical analysis, qualitative researchers may use the hypotheses to guide data collection and analysis, seeking to uncover patterns, themes, or relationships within the qualitative data. The emphasis in qualitative research is often on generating insights and understanding rather than confirming or rejecting specific research hypotheses through statistical testing.
Researcher.Life is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Researcher.Life All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 21+ years of experience in academia, Researcher.Life All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $17 a month !
Related Posts

What is Research? Definition, Types, Methods, and Examples

Turabian Format: A Beginner’s Guide
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Research Hypothesis: What It Is, Types + How to Develop?

A research study starts with a question. Researchers worldwide ask questions and create research hypotheses. The effectiveness of research relies on developing a good research hypothesis. Examples of research hypotheses can guide researchers in writing effective ones.
In this blog, we’ll learn what a research hypothesis is, why it’s important in research, and the different types used in science. We’ll also guide you through creating your research hypothesis and discussing ways to test and evaluate it.
What is a Research Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is like a guess or idea that you suggest to check if it’s true. A research hypothesis is a statement that brings up a question and predicts what might happen.
It’s really important in the scientific method and is used in experiments to figure things out. Essentially, it’s an educated guess about how things are connected in the research.
A research hypothesis usually includes pointing out the independent variable (the thing they’re changing or studying) and the dependent variable (the result they’re measuring or watching). It helps plan how to gather and analyze data to see if there’s evidence to support or deny the expected connection between these variables.
Importance of Hypothesis in Research
Hypotheses are really important in research. They help design studies, allow for practical testing, and add to our scientific knowledge. Their main role is to organize research projects, making them purposeful, focused, and valuable to the scientific community. Let’s look at some key reasons why they matter:
- A research hypothesis helps test theories.
A hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method by providing a basis for testing existing theories. For example, a hypothesis might test the predictive power of a psychological theory on human behavior.
- It serves as a great platform for investigation activities.
It serves as a launching pad for investigation activities, which offers researchers a clear starting point. A research hypothesis can explore the relationship between exercise and stress reduction.
- Hypothesis guides the research work or study.
A well-formulated hypothesis guides the entire research process. It ensures that the study remains focused and purposeful. For instance, a hypothesis about the impact of social media on interpersonal relationships provides clear guidance for a study.
- Hypothesis sometimes suggests theories.
In some cases, a hypothesis can suggest new theories or modifications to existing ones. For example, a hypothesis testing the effectiveness of a new drug might prompt a reconsideration of current medical theories.
- It helps in knowing the data needs.
A hypothesis clarifies the data requirements for a study, ensuring that researchers collect the necessary information—a hypothesis guiding the collection of demographic data to analyze the influence of age on a particular phenomenon.
- The hypothesis explains social phenomena.
Hypotheses are instrumental in explaining complex social phenomena. For instance, a hypothesis might explore the relationship between economic factors and crime rates in a given community.
- Hypothesis provides a relationship between phenomena for empirical Testing.
Hypotheses establish clear relationships between phenomena, paving the way for empirical testing. An example could be a hypothesis exploring the correlation between sleep patterns and academic performance.
- It helps in knowing the most suitable analysis technique.
A hypothesis guides researchers in selecting the most appropriate analysis techniques for their data. For example, a hypothesis focusing on the effectiveness of a teaching method may lead to the choice of statistical analyses best suited for educational research.
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a specific idea that you can test in a study. It often comes from looking at past research and theories. A good hypothesis usually starts with a research question that you can explore through background research. For it to be effective, consider these key characteristics:
- Clear and Focused Language: A good hypothesis uses clear and focused language to avoid confusion and ensure everyone understands it.
- Related to the Research Topic: The hypothesis should directly relate to the research topic, acting as a bridge between the specific question and the broader study.
- Testable: An effective hypothesis can be tested, meaning its prediction can be checked with real data to support or challenge the proposed relationship.
- Potential for Exploration: A good hypothesis often comes from a research question that invites further exploration. Doing background research helps find gaps and potential areas to investigate.
- Includes Variables: The hypothesis should clearly state both the independent and dependent variables, specifying the factors being studied and the expected outcomes.
- Ethical Considerations: Check if variables can be manipulated without breaking ethical standards. It’s crucial to maintain ethical research practices.
- Predicts Outcomes: The hypothesis should predict the expected relationship and outcome, acting as a roadmap for the study and guiding data collection and analysis.
- Simple and Concise: A good hypothesis avoids unnecessary complexity and is simple and concise, expressing the essence of the proposed relationship clearly.
- Clear and Assumption-Free: The hypothesis should be clear and free from assumptions about the reader’s prior knowledge, ensuring universal understanding.
- Observable and Testable Results: A strong hypothesis implies research that produces observable and testable results, making sure the study’s outcomes can be effectively measured and analyzed.
When you use these characteristics as a checklist, it can help you create a good research hypothesis. It’ll guide improving and strengthening the hypothesis, identifying any weaknesses, and making necessary changes. Crafting a hypothesis with these features helps you conduct a thorough and insightful research study.
Types of Research Hypotheses
The research hypothesis comes in various types, each serving a specific purpose in guiding the scientific investigation. Knowing the differences will make it easier for you to create your own hypothesis. Here’s an overview of the common types:
01. Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states that there is no connection between two considered variables or that two groups are unrelated. As discussed earlier, a hypothesis is an unproven assumption lacking sufficient supporting data. It serves as the statement researchers aim to disprove. It is testable, verifiable, and can be rejected.
For example, if you’re studying the relationship between Project A and Project B, assuming both projects are of equal standard is your null hypothesis. It needs to be specific for your study.
02. Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is basically another option to the null hypothesis. It involves looking for a significant change or alternative that could lead you to reject the null hypothesis. It’s a different idea compared to the null hypothesis.
When you create a null hypothesis, you’re making an educated guess about whether something is true or if there’s a connection between that thing and another variable. If the null view suggests something is correct, the alternative hypothesis says it’s incorrect.
For instance, if your null hypothesis is “I’m going to be $1000 richer,” the alternative hypothesis would be “I’m not going to get $1000 or be richer.”
03. Directional Hypothesis
The directional hypothesis predicts the direction of the relationship between independent and dependent variables. They specify whether the effect will be positive or negative.
If you increase your study hours, you will experience a positive association with your exam scores. This hypothesis suggests that as you increase the independent variable (study hours), there will also be an increase in the dependent variable (exam scores).
04. Non-directional Hypothesis
The non-directional hypothesis predicts the existence of a relationship between variables but does not specify the direction of the effect. It suggests that there will be a significant difference or relationship, but it does not predict the nature of that difference.
For example, you will find no notable difference in test scores between students who receive the educational intervention and those who do not. However, once you compare the test scores of the two groups, you will notice an important difference.
05. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis predicts a relationship between one dependent variable and one independent variable without specifying the nature of that relationship. It’s simple and usually used when we don’t know much about how the two things are connected.
For example, if you adopt effective study habits, you will achieve higher exam scores than those with poor study habits.
06. Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is an idea that specifies a relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. It is a more detailed idea than a simple hypothesis.
While a simple view suggests a straightforward cause-and-effect relationship between two things, a complex hypothesis involves many factors and how they’re connected to each other.
For example, when you increase your study time, you tend to achieve higher exam scores. The connection between your study time and exam performance is affected by various factors, including the quality of your sleep, your motivation levels, and the effectiveness of your study techniques.
If you sleep well, stay highly motivated, and use effective study strategies, you may observe a more robust positive correlation between the time you spend studying and your exam scores, unlike those who may lack these factors.
07. Associative Hypothesis
An associative hypothesis proposes a connection between two things without saying that one causes the other. Basically, it suggests that when one thing changes, the other changes too, but it doesn’t claim that one thing is causing the change in the other.
For example, you will likely notice higher exam scores when you increase your study time. You can recognize an association between your study time and exam scores in this scenario.
Your hypothesis acknowledges a relationship between the two variables—your study time and exam scores—without asserting that increased study time directly causes higher exam scores. You need to consider that other factors, like motivation or learning style, could affect the observed association.
08. Causal Hypothesis
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables. It suggests that changes in one variable directly cause changes in another variable.
For example, when you increase your study time, you experience higher exam scores. This hypothesis suggests a direct cause-and-effect relationship, indicating that the more time you spend studying, the higher your exam scores. It assumes that changes in your study time directly influence changes in your exam performance.
09. Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement based on things we can see and measure. It comes from direct observation or experiments and can be tested with real-world evidence. If an experiment proves a theory, it supports the idea and shows it’s not just a guess. This makes the statement more reliable than a wild guess.
For example, if you increase the dosage of a certain medication, you might observe a quicker recovery time for patients. Imagine you’re in charge of a clinical trial. In this trial, patients are given varying dosages of the medication, and you measure and compare their recovery times. This allows you to directly see the effects of different dosages on how fast patients recover.
This way, you can create a research hypothesis: “Increasing the dosage of a certain medication will lead to a faster recovery time for patients.”
10. Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement or assumption about a population parameter that is the subject of an investigation. It serves as the basis for statistical analysis and testing. It is often tested using statistical methods to draw inferences about the larger population.
In a hypothesis test, statistical evidence is collected to either reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis or fail to reject the null hypothesis due to insufficient evidence.
For example, let’s say you’re testing a new medicine. Your hypothesis could be that the medicine doesn’t really help patients get better. So, you collect data and use statistics to see if your guess is right or if the medicine actually makes a difference.
If the data strongly shows that the medicine does help, you say your guess was wrong, and the medicine does make a difference. But if the proof isn’t strong enough, you can stick with your original guess because you didn’t get enough evidence to change your mind.
How to Develop a Research Hypotheses?
Step 1: identify your research problem or topic..
Define the area of interest or the problem you want to investigate. Make sure it’s clear and well-defined.
Start by asking a question about your chosen topic. Consider the limitations of your research and create a straightforward problem related to your topic. Once you’ve done that, you can develop and test a hypothesis with evidence.
Step 2: Conduct a literature review
Review existing literature related to your research problem. This will help you understand the current state of knowledge in the field, identify gaps, and build a foundation for your hypothesis. Consider the following questions:
- What existing research has been conducted on your chosen topic?
- Are there any gaps or unanswered questions in the current literature?
- How will the existing literature contribute to the foundation of your research?
Step 3: Formulate your research question
Based on your literature review, create a specific and concise research question that addresses your identified problem. Your research question should be clear, focused, and relevant to your field of study.
Step 4: Identify variables
Determine the key variables involved in your research question. Variables are the factors or phenomena that you will study and manipulate to test your hypothesis.
- Independent Variable: The variable you manipulate or control.
- Dependent Variable: The variable you measure to observe the effect of the independent variable.
Step 5: State the Null hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no significant difference or effect. It serves as a baseline for comparison with the alternative hypothesis.
Step 6: Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis
Choose research methods that align with your study objectives, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies. The selected methods enable you to test your research hypothesis effectively.
Creating a research hypothesis usually takes more than one try. Expect to make changes as you collect data. It’s normal to test and say no to a few hypotheses before you find the right answer to your research question.
Testing and Evaluating Hypotheses
Testing hypotheses is a really important part of research. It’s like the practical side of things. Here, real-world evidence will help you determine how different things are connected. Let’s explore the main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis.
Before testing, clearly articulate your research hypothesis. This involves framing both a null hypothesis, suggesting no significant effect or relationship, and an alternative hypothesis, proposing the expected outcome.
- Collect data strategically.
Plan how you will gather information in a way that fits your study. Make sure your data collection method matches the things you’re studying.
Whether through surveys, observations, or experiments, this step demands precision and adherence to the established methodology. The quality of data collected directly influences the credibility of study outcomes.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test.
Choose a statistical test that aligns with the nature of your data and the hypotheses being tested. Whether it’s a t-test, chi-square test, ANOVA, or regression analysis, selecting the right statistical tool is paramount for accurate and reliable results.
- Decide if your idea was right or wrong.
Following the statistical analysis, evaluate the results in the context of your null hypothesis. You need to decide if you should reject your null hypothesis or not.
- Share what you found.
When discussing what you found in your research, be clear and organized. Say whether your idea was supported or not, and talk about what your results mean. Also, mention any limits to your study and suggest ideas for future research.
The Role of QuestionPro to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
QuestionPro is a survey and research platform that provides tools for creating, distributing, and analyzing surveys. It plays a crucial role in the research process, especially when you’re in the initial stages of hypothesis development. Here’s how QuestionPro can help you to develop a good research hypothesis:
- Survey design and data collection: You can use the platform to create targeted questions that help you gather relevant data.
- Exploratory research: Through surveys and feedback mechanisms on QuestionPro, you can conduct exploratory research to understand the landscape of a particular subject.
- Literature review and background research: QuestionPro surveys can collect sample population opinions, experiences, and preferences. This data and a thorough literature evaluation can help you generate a well-grounded hypothesis by improving your research knowledge.
- Identifying variables: Using targeted survey questions, you can identify relevant variables related to their research topic.
- Testing assumptions: You can use surveys to informally test certain assumptions or hypotheses before formalizing a research hypothesis.
- Data analysis tools: QuestionPro provides tools for analyzing survey data. You can use these tools to identify the collected data’s patterns, correlations, or trends.
- Refining your hypotheses: As you collect data through QuestionPro, you can adjust your hypotheses based on the real-world responses you receive.
A research hypothesis is like a guide for researchers in science. It’s a well-thought-out idea that has been thoroughly tested. This idea is crucial as researchers can explore different fields, such as medicine, social sciences, and natural sciences. The research hypothesis links theories to real-world evidence and gives researchers a clear path to explore and make discoveries.
QuestionPro Research Suite is a helpful tool for researchers. It makes creating surveys, collecting data, and analyzing information easily. It supports all kinds of research, from exploring new ideas to forming hypotheses. With a focus on using data, it helps researchers do their best work.
Are you interested in learning more about QuestionPro Research Suite? Take advantage of QuestionPro’s free trial to get an initial look at its capabilities and realize the full potential of your research efforts.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

QuestionPro Thrive: A Space to Visualize & Share the Future of Technology
Jun 18, 2024

Relationship NPS Fails to Understand Customer Experiences — Tuesday CX

CX Platform: Top 13 CX Platforms to Drive Customer Success
Jun 17, 2024

How to Know Whether Your Employee Initiatives are Working
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
| Research question | Hypothesis | Null hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
| What are the health benefits of eating an apple a day? | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will result in decreasing frequency of doctor’s visits. | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will have no effect on frequency of doctor’s visits. |
| Which airlines have the most delays? | Low-cost airlines are more likely to have delays than premium airlines. | Low-cost and premium airlines are equally likely to have delays. |
| Can flexible work arrangements improve job satisfaction? | Employees who have flexible working hours will report greater job satisfaction than employees who work fixed hours. | There is no relationship between working hour flexibility and job satisfaction. |
| How effective is secondary school sex education at reducing teen pregnancies? | Teenagers who received sex education lessons throughout secondary school will have lower rates of unplanned pregnancy than teenagers who did not receive any sex education. | Secondary school sex education has no effect on teen pregnancy rates. |
| What effect does daily use of social media have on the attention span of under-16s? | There is a negative correlation between time spent on social media and attention span in under-16s. | There is no relationship between social media use and attention span in under-16s. |
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 18 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
- 4 minute read
- 328.5K views
Table of Contents
One of the most important aspects of conducting research is constructing a strong hypothesis. But what makes a hypothesis in research effective? In this article, we’ll look at the difference between a hypothesis and a research question, as well as the elements of a good hypothesis in research. We’ll also include some examples of effective hypotheses, and what pitfalls to avoid.
What is a Hypothesis in Research?
Simply put, a hypothesis is a research question that also includes the predicted or expected result of the research. Without a hypothesis, there can be no basis for a scientific or research experiment. As such, it is critical that you carefully construct your hypothesis by being deliberate and thorough, even before you set pen to paper. Unless your hypothesis is clearly and carefully constructed, any flaw can have an adverse, and even grave, effect on the quality of your experiment and its subsequent results.
Research Question vs Hypothesis
It’s easy to confuse research questions with hypotheses, and vice versa. While they’re both critical to the Scientific Method, they have very specific differences. Primarily, a research question, just like a hypothesis, is focused and concise. But a hypothesis includes a prediction based on the proposed research, and is designed to forecast the relationship of and between two (or more) variables. Research questions are open-ended, and invite debate and discussion, while hypotheses are closed, e.g. “The relationship between A and B will be C.”
A hypothesis is generally used if your research topic is fairly well established, and you are relatively certain about the relationship between the variables that will be presented in your research. Since a hypothesis is ideally suited for experimental studies, it will, by its very existence, affect the design of your experiment. The research question is typically used for new topics that have not yet been researched extensively. Here, the relationship between different variables is less known. There is no prediction made, but there may be variables explored. The research question can be casual in nature, simply trying to understand if a relationship even exists, descriptive or comparative.
How to Write Hypothesis in Research
Writing an effective hypothesis starts before you even begin to type. Like any task, preparation is key, so you start first by conducting research yourself, and reading all you can about the topic that you plan to research. From there, you’ll gain the knowledge you need to understand where your focus within the topic will lie.
Remember that a hypothesis is a prediction of the relationship that exists between two or more variables. Your job is to write a hypothesis, and design the research, to “prove” whether or not your prediction is correct. A common pitfall is to use judgments that are subjective and inappropriate for the construction of a hypothesis. It’s important to keep the focus and language of your hypothesis objective.
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions.
Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis:
- Predicts the relationship and outcome
- Simple and concise – avoid wordiness
- Clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Observable and testable results
- Relevant and specific to the research question or problem
Research Hypothesis Example
Perhaps the best way to evaluate whether or not your hypothesis is effective is to compare it to those of your colleagues in the field. There is no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing a powerful research hypothesis. As you’re reading and preparing your hypothesis, you’ll also read other hypotheses. These can help guide you on what works, and what doesn’t, when it comes to writing a strong research hypothesis.
Here are a few generic examples to get you started.
Eating an apple each day, after the age of 60, will result in a reduction of frequency of physician visits.
Budget airlines are more likely to receive more customer complaints. A budget airline is defined as an airline that offers lower fares and fewer amenities than a traditional full-service airline. (Note that the term “budget airline” is included in the hypothesis.
Workplaces that offer flexible working hours report higher levels of employee job satisfaction than workplaces with fixed hours.
Each of the above examples are specific, observable and measurable, and the statement of prediction can be verified or shown to be false by utilizing standard experimental practices. It should be noted, however, that often your hypothesis will change as your research progresses.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier’s Language Editing Plus service can help ensure that your research hypothesis is well-designed, and articulates your research and conclusions. Our most comprehensive editing package, you can count on a thorough language review by native-English speakers who are PhDs or PhD candidates. We’ll check for effective logic and flow of your manuscript, as well as document formatting for your chosen journal, reference checks, and much more.

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?

What is a Problem Statement? [with examples]
You may also like.

Page-Turner Articles are More Than Just Good Arguments: Be Mindful of Tone and Structure!

A Must-see for Researchers! How to Ensure Inclusivity in Your Scientific Writing

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
13 Different Types of Hypothesis

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
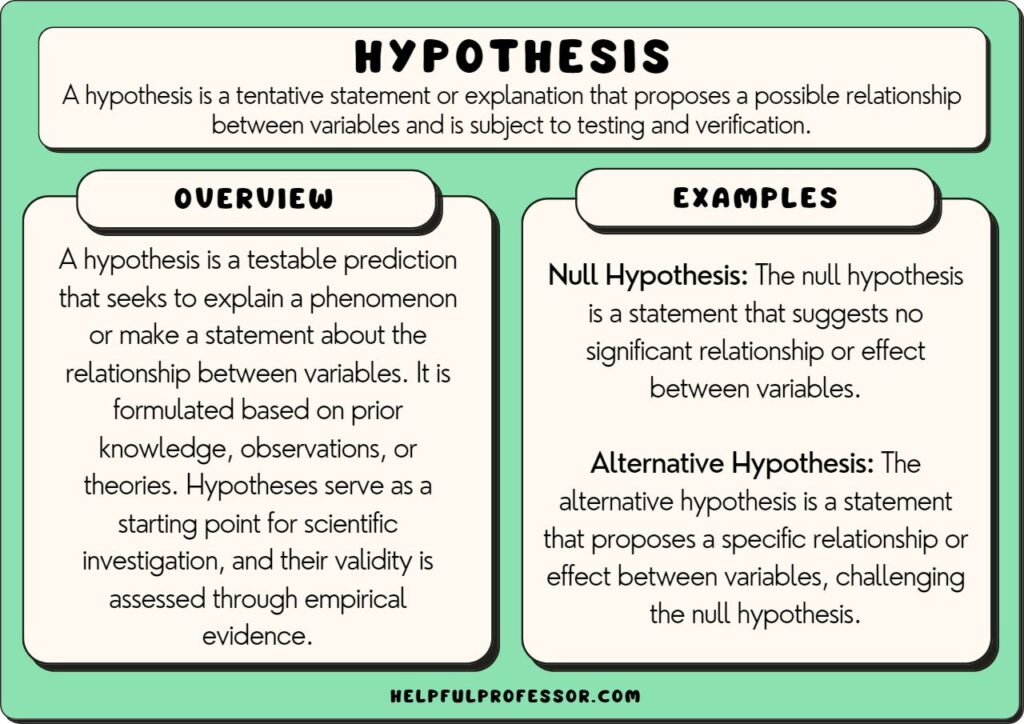
There are 13 different types of hypothesis. These include simple, complex, null, alternative, composite, directional, non-directional, logical, empirical, statistical, associative, exact, and inexact.
A hypothesis can be categorized into one or more of these types. However, some are mutually exclusive and opposites. Simple and complex hypotheses are mutually exclusive, as are direction and non-direction, and null and alternative hypotheses.
Below I explain each hypothesis in simple terms for absolute beginners. These definitions may be too simple for some, but they’re designed to be clear introductions to the terms to help people wrap their heads around the concepts early on in their education about research methods .
Types of Hypothesis
Before you Proceed: Dependent vs Independent Variables
A research study and its hypotheses generally examine the relationships between independent and dependent variables – so you need to know these two concepts:
- The independent variable is the variable that is causing a change.
- The dependent variable is the variable the is affected by the change. This is the variable being tested.
Read my full article on dependent vs independent variables for more examples.
Example: Eating carrots (independent variable) improves eyesight (dependent variable).
1. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a hypothesis that predicts a correlation between two test variables: an independent and a dependent variable.
This is the easiest and most straightforward type of hypothesis. You simply need to state an expected correlation between the dependant variable and the independent variable.
You do not need to predict causation (see: directional hypothesis). All you would need to do is prove that the two variables are linked.
Simple Hypothesis Examples
| Question | Simple Hypothesis |
|---|---|
| Do people over 50 like Coca-Cola more than people under 50? | On average, people over 50 like Coca-Cola more than people under 50. |
| According to national registries of car accident data, are Canadians better drivers than Americans? | Canadians are better drivers than Americans. |
| Are carpenters more liberal than plumbers? | Carpenters are more liberal than plumbers. |
| Do guitarists live longer than pianists? | Guitarists do live longer than pianists. |
| Do dogs eat more in summer than winter? | Dogs do eat more in summer than winter. |
2. Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a hypothesis that contains multiple variables, making the hypothesis more specific but also harder to prove.
You can have multiple independent and dependant variables in this hypothesis.
Complex Hypothesis Example
| Question | Complex Hypothesis |
|---|---|
| Do (1) age and (2) weight affect chances of getting (3) diabetes and (4) heart disease? | (1) Age and (2) weight increase your chances of getting (3) diabetes and (4) heart disease. |
In the above example, we have multiple independent and dependent variables:
- Independent variables: Age and weight.
- Dependent variables: diabetes and heart disease.
Because there are multiple variables, this study is a lot more complex than a simple hypothesis. It quickly gets much more difficult to prove these hypotheses. This is why undergraduate and first-time researchers are usually encouraged to use simple hypotheses.
3. Null Hypothesis
A null hypothesis will predict that there will be no significant relationship between the two test variables.
For example, you can say that “The study will show that there is no correlation between marriage and happiness.”
A good way to think about a null hypothesis is to think of it in the same way as “innocent until proven guilty”[1]. Unless you can come up with evidence otherwise, your null hypothesis will stand.
A null hypothesis may also highlight that a correlation will be inconclusive . This means that you can predict that the study will not be able to confirm your results one way or the other. For example, you can say “It is predicted that the study will be unable to confirm a correlation between the two variables due to foreseeable interference by a third variable .”
Beware that an inconclusive null hypothesis may be questioned by your teacher. Why would you conduct a test that you predict will not provide a clear result? Perhaps you should take a closer look at your methodology and re-examine it. Nevertheless, inconclusive null hypotheses can sometimes have merit.
Null Hypothesis Examples
| Question | Null Hypothesis (H ) |
|---|---|
| Do people over 50 like Coca-Cola more than people under 50? | Age has no effect on preference for Coca-Cola. |
| Are Canadians better drivers than Americans? | Nationality has no effect on driving ability. |
| Are carpenters more liberal than plumbers? | There is no statistically significant difference in political views between carpenters and plumbers. |
| Do guitarists live longer than pianists? | There is no statistically significant difference in life expectancy between guitarists and pianists. |
| Do dogs eat more in summer than winter? | Time of year has no effect on dogs’ appetites. |
4. Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a hypothesis that is anything other than the null hypothesis. It will disprove the null hypothesis.
We use the symbol H A or H 1 to denote an alternative hypothesis.
The null and alternative hypotheses are usually used together. We will say the null hypothesis is the case where a relationship between two variables is non-existent. The alternative hypothesis is the case where there is a relationship between those two variables.
The following statement is always true: H 0 ≠ H A .
Let’s take the example of the hypothesis: “Does eating oatmeal before an exam impact test scores?”
We can have two hypotheses here:
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): “Eating oatmeal before an exam does not impact test scores.”
- Alternative hypothesis (H A ): “Eating oatmeal before an exam does impact test scores.”
For the alternative hypothesis to be true, all we have to do is disprove the null hypothesis for the alternative hypothesis to be true. We do not need an exact prediction of how much oatmeal will impact the test scores or even if the impact is positive or negative. So long as the null hypothesis is proven to be false, then the alternative hypothesis is proven to be true.
5. Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a hypothesis that does not predict the exact parameters, distribution, or range of the dependent variable.
Often, we would predict an exact outcome. For example: “23 year old men are on average 189cm tall.” Here, we are giving an exact parameter. So, the hypothesis is not composite.
But, often, we cannot exactly hypothesize something. We assume that something will happen, but we’re not exactly sure what. In these cases, we might say: “23 year old men are not on average 189cm tall.”
We haven’t set a distribution range or exact parameters of the average height of 23 year old men. So, we’ve introduced a composite hypothesis as opposed to an exact hypothesis.
Generally, an alternative hypothesis (discussed above) is composite because it is defined as anything except the null hypothesis. This ‘anything except’ does not define parameters or distribution, and therefore it’s an example of a composite hypothesis.

6. Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis makes a prediction about the positivity or negativity of the effect of an intervention prior to the test being conducted.
Instead of being agnostic about whether the effect will be positive or negative, it nominates the effect’s directionality.
We often call this a one-tailed hypothesis (in contrast to a two-tailed or non-directional hypothesis) because, looking at a distribution graph, we’re hypothesizing that the results will lean toward one particular tail on the graph – either the positive or negative.
Directional Hypothesis Examples
| Question | Directional Hypothesis |
|---|---|
| Does adding a 10c charge to plastic bags at grocery stores lead to changes in uptake of reusable bags? | Adding a 10c charge to plastic bags in grocery stores will lead to an in uptake of reusable bags. |
| Does a Universal Basic Income influence retail worker wages? | Universal Basic Income retail worker wages. |
| Does rainy weather impact the amount of moderate to high intensity exercise people do per week in the city of Vancouver? | Rainy weather the amount of moderate to high intensity exercise people do per week in the city of Vancouver. |
| Does introducing fluoride to the water system in the city of Austin impact number of dental visits per capita per year? | Introducing fluoride to the water system in the city of Austin the number of dental visits per capita per year? |
| Does giving children chocolate rewards during study time for positive answers impact standardized test scores? | Giving children chocolate rewards during study time for positive answers standardized test scores. |
7. Non-Directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis does not specify the predicted direction (e.g. positivity or negativity) of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
These hypotheses predict an effect, but stop short of saying what that effect will be.
A non-directional hypothesis is similar to composite and alternative hypotheses. All three types of hypothesis tend to make predictions without defining a direction. In a composite hypothesis, a specific prediction is not made (although a general direction may be indicated, so the overlap is not complete). For an alternative hypothesis, you often predict that the even will be anything but the null hypothesis, which means it could be more or less than H 0 (or in other words, non-directional).
Let’s turn the above directional hypotheses into non-directional hypotheses.
Non-Directional Hypothesis Examples
| Question | Non-Directional Hypothesis |
|---|---|
| Does adding a 10c charge to plastic bags at grocery stores lead to changes in uptake of reusable bags? | Adding a 10c charge to plastic bags in grocery stores will lead to a in uptake of reusable bags. |
| Does a Universal Basic Income influence retail worker wages? | Universal Basic Income retail worker wages. |
| Does rainy weather impact the amount of moderate to high intensity exercise people do per week in the city of Vancouver? | Rainy weather the amount of moderate to high intensity exercise people do per week in the city of Vancouver. |
| Does introducing fluoride to the water system in the city of Austin impact number of dental visits per capita per year? | Introducing fluoride to the water system in the city of Austin the number of dental visits per capita per year? |
| Does giving children chocolate rewards during study time for positive answers impact standardized test scores? | Giving children chocolate rewards during study time for positive answers standardized test scores. |
8. Logical Hypothesis
A logical hypothesis is a hypothesis that cannot be tested, but has some logical basis underpinning our assumptions.
These are most commonly used in philosophy because philosophical questions are often untestable and therefore we must rely on our logic to formulate logical theories.
Usually, we would want to turn a logical hypothesis into an empirical one through testing if we got the chance. Unfortunately, we don’t always have this opportunity because the test is too complex, expensive, or simply unrealistic.
Here are some examples:
- Before the 1980s, it was hypothesized that the Titanic came to its resting place at 41° N and 49° W, based on the time the ship sank and the ship’s presumed path across the Atlantic Ocean. However, due to the depth of the ocean, it was impossible to test. Thus, the hypothesis was simply a logical hypothesis.
- Dinosaurs closely related to Aligators probably had green scales because Aligators have green scales. However, as they are all extinct, we can only rely on logic and not empirical data.
9. Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is the opposite of a logical hypothesis. It is a hypothesis that is currently being tested using scientific analysis. We can also call this a ‘working hypothesis’.
We can to separate research into two types: theoretical and empirical. Theoretical research relies on logic and thought experiments. Empirical research relies on tests that can be verified by observation and measurement.
So, an empirical hypothesis is a hypothesis that can and will be tested.
- Raising the wage of restaurant servers increases staff retention.
- Adding 1 lb of corn per day to cows’ diets decreases their lifespan.
- Mushrooms grow faster at 22 degrees Celsius than 27 degrees Celsius.
Each of the above hypotheses can be tested, making them empirical rather than just logical (aka theoretical).
10. Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis utilizes representative statistical models to draw conclusions about broader populations.
It requires the use of datasets or carefully selected representative samples so that statistical inference can be drawn across a larger dataset.
This type of research is necessary when it is impossible to assess every single possible case. Imagine, for example, if you wanted to determine if men are taller than women. You would be unable to measure the height of every man and woman on the planet. But, by conducting sufficient random samples, you would be able to predict with high probability that the results of your study would remain stable across the whole population.
You would be right in guessing that almost all quantitative research studies conducted in academic settings today involve statistical hypotheses.
Statistical Hypothesis Examples
- Human Sex Ratio. The most famous statistical hypothesis example is that of John Arbuthnot’s sex at birth case study in 1710. Arbuthnot used birth data to determine with high statistical probability that there are more male births than female births. He called this divine providence, and to this day, his findings remain true: more men are born than women.
- Lady Testing Tea. A 1935 study by Ronald Fisher involved testing a woman who believed she could tell whether milk was added before or after water to a cup of tea. Fisher gave her 4 cups in which one randomly had milk placed before the tea. He repeated the test 8 times. The lady was correct each time. Fisher found that she had a 1 in 70 chance of getting all 8 test correct, which is a statistically significant result.
11. Associative Hypothesis
An associative hypothesis predicts that two variables are linked but does not explore whether one variable directly impacts upon the other variable.
We commonly refer to this as “ correlation does not mean causation ”. Just because there are a lot of sick people in a hospital, it doesn’t mean that the hospital made the people sick. There is something going on there that’s causing the issue (sick people are flocking to the hospital).
So, in an associative hypothesis, you note correlation between an independent and dependent variable but do not make a prediction about how the two interact. You stop short of saying one thing causes another thing.
Associative Hypothesis Examples
- Sick people in hospital. You could conduct a study hypothesizing that hospitals have more sick people in them than other institutions in society. However, you don’t hypothesize that the hospitals caused the sickness.
- Lice make you healthy. In the Middle Ages, it was observed that sick people didn’t tend to have lice in their hair. The inaccurate conclusion was that lice was not only a sign of health, but that they made people healthy. In reality, there was an association here, but not causation. The fact was that lice were sensitive to body temperature and fled bodies that had fevers.
12. Causal Hypothesis
A causal hypothesis predicts that two variables are not only associated, but that changes in one variable will cause changes in another.
A causal hypothesis is harder to prove than an associative hypothesis because the cause needs to be definitively proven. This will often require repeating tests in controlled environments with the researchers making manipulations to the independent variable, or the use of control groups and placebo effects .
If we were to take the above example of lice in the hair of sick people, researchers would have to put lice in sick people’s hair and see if it made those people healthier. Researchers would likely observe that the lice would flee the hair, but the sickness would remain, leading to a finding of association but not causation.
Causal Hypothesis Examples
| Question | Causation Hypothesis | Correlation Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
| Does marriage cause baldness among men? | Marriage causes stress which leads to hair loss. | Marriage occurs at an age when men naturally start balding. |
| What is the relationship between recreational drugs and psychosis? | Recreational drugs cause psychosis. | People with psychosis take drugs to self-medicate. |
| Do ice cream sales lead to increase drownings? | Ice cream sales cause increased drownings. | Ice cream sales peak during summer, when more people are swimming and therefore more drownings are occurring. |
13. Exact vs. Inexact Hypothesis
For brevity’s sake, I have paired these two hypotheses into the one point. The reality is that we’ve already seen both of these types of hypotheses at play already.
An exact hypothesis (also known as a point hypothesis) specifies a specific prediction whereas an inexact hypothesis assumes a range of possible values without giving an exact outcome. As Helwig [2] argues:
“An “exact” hypothesis specifies the exact value(s) of the parameter(s) of interest, whereas an “inexact” hypothesis specifies a range of possible values for the parameter(s) of interest.”
Generally, a null hypothesis is an exact hypothesis whereas alternative, composite, directional, and non-directional hypotheses are all inexact.
See Next: 15 Hypothesis Examples
This is introductory information that is basic and indeed quite simplified for absolute beginners. It’s worth doing further independent research to get deeper knowledge of research methods and how to conduct an effective research study. And if you’re in education studies, don’t miss out on my list of the best education studies dissertation ideas .
[1] https://jnnp.bmj.com/content/91/6/571.abstract
[2] http://users.stat.umn.edu/~helwig/notes/SignificanceTesting.pdf

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
2 thoughts on “13 Different Types of Hypothesis”
Wow! This introductionary materials are very helpful. I teach the begginers in research for the first time in my career. The given tips and materials are very helpful. Chris, thank you so much! Excellent materials!

You’re more than welcome! If you want a pdf version of this article to provide for your students to use as a weekly reading on in-class discussion prompt for seminars, just drop me an email in the Contact form and I’ll get one sent out to you.
When I’ve taught this seminar, I’ve put my students into groups, cut these definitions into strips, and handed them out to the groups. Then I get them to try to come up with hypotheses that fit into each ‘type’. You can either just rotate hypothesis types so they get a chance at creating a hypothesis of each type, or get them to “teach” their hypothesis type and examples to the class at the end of the seminar.
Cheers, Chris
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- How it works

How to Write a Hypothesis – Steps & Tips
Published by Alaxendra Bets at August 14th, 2021 , Revised On October 26, 2023
What is a Research Hypothesis?
You can test a research statement with the help of experimental or theoretical research, known as a hypothesis.
If you want to find out the similarities, differences, and relationships between variables, you must write a testable hypothesis before compiling the data, performing analysis, and generating results to complete.
The data analysis and findings will help you test the hypothesis and see whether it is true or false. Here is all you need to know about how to write a hypothesis for a dissertation .
Research Hypothesis Definition
Not sure what the meaning of the research hypothesis is?
A research hypothesis predicts an answer to the research question based on existing theoretical knowledge or experimental data.
Some studies may have multiple hypothesis statements depending on the research question(s). A research hypothesis must be based on formulas, facts, and theories. It should be testable by data analysis, observations, experiments, or other scientific methodologies that can refute or support the statement.
Variables in Hypothesis
Developing a hypothesis is easy. Most research studies have two or more variables in the hypothesis, particularly studies involving correlational and experimental research. The researcher can control or change the independent variable(s) while measuring and observing the independent variable(s).
“How long a student sleeps affects test scores.”
In the above statement, the dependent variable is the test score, while the independent variable is the length of time spent in sleep. Developing a hypothesis will be easy if you know your research’s dependent and independent variables.
Once you have developed a thesis statement, questions such as how to write a hypothesis for the dissertation and how to test a research hypothesis become pretty straightforward.
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with quantitative dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Step-by-Step Guide on How to Write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps involved in how to write a hypothesis for a dissertation.
Step 1: Start with a Research Question
- Begin by asking a specific question about a topic of interest.
- This question should be clear, concise, and researchable.
Example: Does exposure to sunlight affect plant growth?
Step 2: Do Preliminary Research
- Before formulating a hypothesis, conduct background research to understand existing knowledge on the topic.
- Familiarise yourself with prior studies, theories, or observations related to the research question.
Step 3: Define Variables
- Independent Variable (IV): The factor that you change or manipulate in an experiment.
- Dependent Variable (DV): The factor that you measure.
Example: IV: Amount of sunlight exposure (e.g., 2 hours/day, 4 hours/day, 8 hours/day) DV: Plant growth (e.g., height in centimetres)
Step 4: Formulate the Hypothesis
- A hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables.
- It is often written as an “if-then” statement.
Example: If plants receive more sunlight, then they will grow taller.
Step 5: Ensure it is Testable
A good hypothesis is empirically testable. This means you should be able to design an experiment or observation to test its validity.
Example: You can set up an experiment where plants are exposed to varying amounts of sunlight and then measure their growth over a period of time.
Step 6: Consider Potential Confounding Variables
- Confounding variables are factors other than the independent variable that might affect the outcome.
- It is important to identify these to ensure that they do not skew your results.
Example: Soil quality, water frequency, or type of plant can all affect growth. Consider keeping these constant in your experiment.
Step 7: Write the Null Hypothesis
- The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no effect or no relationship between the variables.
- It is what you aim to disprove or reject through your research.
Example: There is no difference in plant growth regardless of the amount of sunlight exposure.
Step 8: Test your Hypothesis
Design an experiment or conduct observations to test your hypothesis.
Example: Grow three sets of plants: one set exposed to 2 hours of sunlight daily, another exposed to 4 hours, and a third exposed to 8 hours. Measure and compare their growth after a set period.
Step 9: Analyse the Results
After testing, review your data to determine if it supports your hypothesis.
Step 10: Draw Conclusions
- Based on your findings, determine whether you can accept or reject the hypothesis.
- Remember, even if you reject your hypothesis, it’s a valuable result. It can guide future research and refine questions.
Three Ways to Phrase a Hypothesis
Try to use “if”… and “then”… to identify the variables. The independent variable should be present in the first part of the hypothesis, while the dependent variable will form the second part of the statement. Consider understanding the below research hypothesis example to create a specific, clear, and concise research hypothesis;
If an obese lady starts attending Zomba fitness classes, her health will improve.
In academic research, you can write the predicted variable relationship directly because most research studies correlate terms.
The number of Zomba fitness classes attended by the obese lady has a positive effect on health.
If your research compares two groups, then you can develop a hypothesis statement on their differences.
An obese lady who attended most Zumba fitness classes will have better health than those who attended a few.
How to Write a Null Hypothesis
If a statistical analysis is involved in your research, then you must create a null hypothesis. If you find any relationship between the variables, then the null hypothesis will be the default position that there is no relationship between them. H0 is the symbol for the null hypothesis, while the hypothesis is represented as H1. The null hypothesis will also answer your question, “How to test the research hypothesis in the dissertation.”
H0: The number of Zumba fitness classes attended by the obese lady does not affect her health.
H1: The number of Zumba fitness classes attended by obese lady positively affects health.
Also see: Your Dissertation in Education
Hypothesis Examples
Research Question: Does the amount of sunlight a plant receives affect its growth? Hypothesis: Plants that receive more sunlight will grow taller than plants that receive less sunlight.
Research Question: Do students who eat breakfast perform better in school exams than those who don’t? Hypothesis: Students who eat a morning breakfast will score higher on school exams compared to students who skip breakfast.
Research Question: Does listening to music while studying impact a student’s ability to retain information? Hypothesis 1 (Directional): Students who listen to music while studying will retain less information than those who study in silence. Hypothesis 2 (Non-directional): There will be a difference in information retention between students who listen to music while studying and those who study in silence.
How can ResearchProspect Help?
If you are unsure about how to rest a research hypothesis in a dissertation or simply unsure about how to develop a hypothesis for your research, then you can take advantage of our dissertation services which cover every tiny aspect of a dissertation project you might need help with including but not limited to setting up a hypothesis and research questions, help with individual chapters , full dissertation writing , statistical analysis , and much more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 rules for writing a good hypothesis.
- Clear Statement: State a clear relationship between variables.
- Testable: Ensure it can be investigated and measured.
- Specific: Avoid vague terms, be precise in predictions.
- Falsifiable: Design to allow potential disproof.
- Relevant: Address research question and align with existing knowledge.
What is a hypothesis in simple words?
A hypothesis is an educated guess or prediction about something that can be tested. It is a statement that suggests a possible explanation for an event or phenomenon based on prior knowledge or observation. Scientists use hypotheses as a starting point for experiments to discover if they are true or false.
What is the hypothesis and examples?
A hypothesis is a testable prediction or explanation for an observation or phenomenon. For example, if plants are given sunlight, then they will grow. In this case, the hypothesis suggests that sunlight has a positive effect on plant growth. It can be tested by experimenting with plants in varying light conditions.
What is the hypothesis in research definition?
A hypothesis in research is a clear, testable statement predicting the possible outcome of a study based on prior knowledge and observation. It serves as the foundation for conducting experiments or investigations. Researchers test the validity of the hypothesis to draw conclusions and advance knowledge in a particular field.
Why is it called a hypothesis?
The term “hypothesis” originates from the Greek word “hypothesis,” which means “base” or “foundation.” It’s used to describe a foundational statement or proposition that can be tested. In scientific contexts, it denotes a tentative explanation for a phenomenon, serving as a starting point for investigation or experimentation.
You May Also Like
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
Not sure how to approach a company for your primary research study? Don’t worry. Here we have some tips for you to successfully gather primary study.
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
)
Published November 23, 2021. Updated December 13, 2021.
A hypothesis is a testable statement based on the researcher’s expectation for the outcome of a study or an observed phenomenon. It helps establish a relationship between two or more variables. A hypothesis acts as the objective of research and guides the researcher to structure experiments that would produce accurate and reliable results. In all likelihood, if a hypothesis is proven by repeatable and reproducible experiments, it may become a theory or even a law of nature.
What is a hypothesis?
A research hypothesis is an educated, clear, specific and falsifiable prediction of the possible outcomes of scientific observation. A hypothesis can be considered as the starting point of research, as any research without it is aimless. For a hypothesis to be complete, it should contain three main elements, i.e., two or more variables, a population, and the correlation between the variables. A hypothesis lays out a path for researchers, directing them how exactly the experiment should be designed, the type of data that should be collected, the sample size for the experiment, and how the data analysis should be performed, along with providing a basis to obtain results and validate them.
Observation and prior knowledge are the primary steps to developing a research hypothesis. For example:
You are watching a race in school and observe the speed with which the winner ran. You may wonder why the winner ran so fast. You may think of a few possibilities which could lead to this result, such as the amount of practice before the race, hours of sleep, or consumption of an energy drink. Since the amount of practice and sleep may almost be constant for all the participants, you may feel the win is because of the consumption of an energy drink. So, you may develop a hypothesis such as “Athletes consuming an energy drink daily perform better.”
Developing a good hypothesis
A hypothesis is important as it helps predict the relationship between two variables, which is essential for conducting your research. In the previous example, the researcher uses the consumption of energy drinks and athlete performance as variables and the athletes as a population while trying to establish the effect of the consumption of an energy drink on the performance of an athlete.
A good hypothesis is central to research for providing reliable and valid results. There are a few points should be kept in mind while formulating your hypothesis. Let’s have a look at them.
1) Ask a question : The foremost step to developing a hypothesis is asking a question. Identifying a question which you are interested in studying is important. For example:
How can air pollution in a region be reduced?
2) Conceptual nature : A hypothesis should be related to a certain concept. This allows the linking of research questions in a study, collecting data, and performing analysis according to the stated concept. For example:
Regions with a greater percentage of tree cover are likely to be less polluted than regions with lower tree cover.
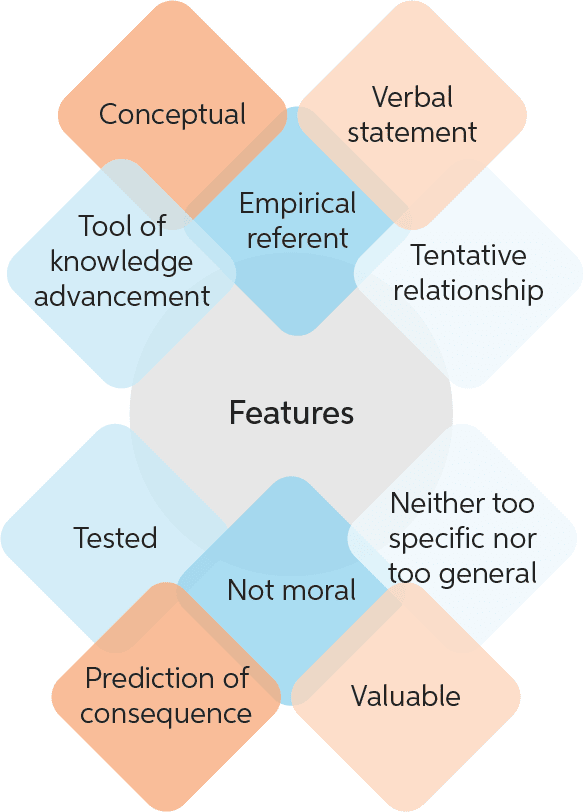
3) Verbal statement : A hypothesis is phrased as a declaration and never as a question. It is the representation of the researcher’s idea or assumption in words that can be tested. For example:
Bad hypothesis: Does following a healthy diet alter the weight of a person?
Good hypothesis: People who follow a healthy diet stay fit.
4) Falsifiable and testable : A hypothesis should be testable so that experiments can be conducted to make observations that agree or disagree with it. It should be falsifiable so that it can be proven wrong if it is found to be incorrect. For example:
Children who use phones while studying score low marks in their exams.
5) Relationship between two variables : A hypothesis suggests a relationship between two or more variables. An independent variable is controlled by the researcher to look at the effects on other variables, i.e., it is the cause for something to happen. A dependent variable is affected by the independent variable and is observed and measured by the researcher. For example:
Consumption of aerated drinks leads to increased blood sugar levels.
Here, the consumption of aerated drinks is the independent variable. The dependent variable is the sugar level that is affected by the consumption of aerated drinks.
6) Specific and precise : A hypothesis should not be too general or vague as obtaining focused results becomes difficult. Also, a hypothesis should not be too specific as it limits the scope of the study. For example:
General: Eating food leads to weight gain.
Specific: Eating ice cream causes weight gain.
Good hypothesis: Consumption of sugar-rich food causes weight in individuals.
If these factors are paid attention to while structuring your hypothesis, you are sure to formulate a sound hypothesis that will direct your research down the correct path.
Types of hypotheses
The hypothesis can be classified into the following categories:
1) Simple Hypothesis : Simple hypotheses draw a relationship between a single independent variable and a single dependent variable. For example:
Increased hours of studying by students leads to them getting better marks.
Here, the hours of study acts as the independent variable while the obtained marks act as the dependent variable.
2) Complex Hypothesis : A complex hypothesis tends to propose a relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. For example:
Increased hours of studying and eight hours of sleep by students result in getting better marks by an increased attention span.
3) Directional Hypothesis : This type of hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of an independent variable on the dependent variable, thus predicting the direction of the effect. For example:
Students scoring good marks in exams tend to have better jobs than the students who score low marks in exams.
Here both the effect and the direction of the effect are represented in the hypothesis.
4) Non-directional Hypothesis : The null hypothesis states a relationship between two variables but does not state the kind of effect that may exist between them. For example:
Students scoring good marks will have jobs different from students scoring low marks.
5) Null Hypothesis : This is a negative statement contrary to the hypothesis and suggests no relationship between the independent and the dependent variable. It is represented as H o . For example:
H o : There is no relationship between hours of study by a student and the earned marks.
H o : Students scoring good and low marks are likely to get similar jobs.
6) Alternative Hypothesis : An alternative to the null hypothesis, it suggests the difference or effect between two or more variables. It is represented as H 1 . For example:
H 1 : There is a relationship between hours of study by a student and the earned marks.
H 1 : Students scoring good and low marks are likely to get different quality jobs.
How to structure a hypothesis?
A hypothesis should be structured in such a way that it should be simple, clear, and easy to understand, and should represent the intent of the hypothesis. There are a few ways to do this:
1) A hypothesis can be represented as a simple ‘if…then’ statement. While the first part of the statement introduces the independent variable, the latter part brings up the dependent variable. For example:
If the plant is watered, then the plant’s growth will improve.
2) A hypothesis can also be written as a statement correlating two variables, directly predicting the relationship between the two variables. For example:
The more times a plant is watered, the better the growth of the plant will be.
3) Another way of structuring a hypothesis is to compare two groups and state the difference expected to occur between the two groups. For example:
Plants that are watered daily are taller than plants that are watered on alternate days.
Testing a hypothesis
Once you have formulated your hypothesis, the next step is to test it to determine if it is correct or incorrect. The steps given below help to test a hypothesis:
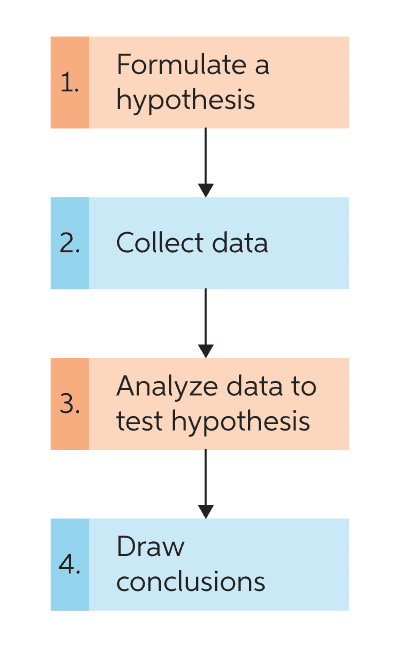
1) State your research hypothesis in the form of a null hypothesis (H o ) and an alternative hypothesis (H 1 ).
2) Perform appropriate experiments and collect data to test the hypothesis.
3) Analyze the data to see whether the hypothesis is supported or refuted.
4) Interpret the data and present your results.
Key takeaways
- A hypothesis is a testable statement based on the researcher’s expectation of an outcome for observed phenomena that is simple, clear, specific, and focuses on only one issue.
- A hypothesis is the focal point of research and directs the course of the research in terms of data collection, sample size, and data analysis.
- A hypothesis is composed of three main components: two or more variables, a population, and the relationship between the variables. Independent and dependent variables are two kinds of variables used while structuring a hypothesis.
- It should be possible to test the hypothesis by performing experiments and prove it to be correct or incorrect.
- A hypothesis helps in testing theories, investigating activities, explaining social phenomena. Further, while acting as a bridge between theory and investigation, it helps determine the most suitable type of research for a problem and allows for the empirical testing of a relationship between variables. If you are lucky, one of your hypotheses may suggest a theory!
Research Process
For more details, visit these additional research guides .
Understand the Research Process
- Research process
- Research questions
- Operationalization
- Research problem
- Statement of the problem
- Background research
- Research hypothesis
- Generalization

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Statistics By Jim
Making statistics intuitive
Hypothesis Testing: Uses, Steps & Example
By Jim Frost 4 Comments
What is Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing in statistics uses sample data to infer the properties of a whole population . These tests determine whether a random sample provides sufficient evidence to conclude an effect or relationship exists in the population. Researchers use them to help separate genuine population-level effects from false effects that random chance can create in samples. These methods are also known as significance testing.

For example, researchers are testing a new medication to see if it lowers blood pressure. They compare a group taking the drug to a control group taking a placebo. If their hypothesis test results are statistically significant, the medication’s effect of lowering blood pressure likely exists in the broader population, not just the sample studied.
Using Hypothesis Tests
A hypothesis test evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement the sample data best supports. These two statements are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . The following are typical examples:
- Null Hypothesis : The effect does not exist in the population.
- Alternative Hypothesis : The effect does exist in the population.
Hypothesis testing accounts for the inherent uncertainty of using a sample to draw conclusions about a population, which reduces the chances of false discoveries. These procedures determine whether the sample data are sufficiently inconsistent with the null hypothesis that you can reject it. If you can reject the null, your data favor the alternative statement that an effect exists in the population.
Statistical significance in hypothesis testing indicates that an effect you see in sample data also likely exists in the population after accounting for random sampling error , variability, and sample size. Your results are statistically significant when the p-value is less than your significance level or, equivalently, when your confidence interval excludes the null hypothesis value.
Conversely, non-significant results indicate that despite an apparent sample effect, you can’t be sure it exists in the population. It could be chance variation in the sample and not a genuine effect.
Learn more about Failing to Reject the Null .
5 Steps of Significance Testing
Hypothesis testing involves five key steps, each critical to validating a research hypothesis using statistical methods:
- Formulate the Hypotheses : Write your research hypotheses as a null hypothesis (H 0 ) and an alternative hypothesis (H A ).
- Data Collection : Gather data specifically aimed at testing the hypothesis.
- Conduct A Test : Use a suitable statistical test to analyze your data.
- Make a Decision : Based on the statistical test results, decide whether to reject the null hypothesis or fail to reject it.
- Report the Results : Summarize and present the outcomes in your report’s results and discussion sections.
While the specifics of these steps can vary depending on the research context and the data type, the fundamental process of hypothesis testing remains consistent across different studies.
Let’s work through these steps in an example!
Hypothesis Testing Example
Researchers want to determine if a new educational program improves student performance on standardized tests. They randomly assign 30 students to a control group , which follows the standard curriculum, and another 30 students to a treatment group, which participates in the new educational program. After a semester, they compare the test scores of both groups.
Download the CSV data file to perform the hypothesis testing yourself: Hypothesis_Testing .
The researchers write their hypotheses. These statements apply to the population, so they use the mu (μ) symbol for the population mean parameter .
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ) : The population means of the test scores for the two groups are equal (μ 1 = μ 2 ).
- Alternative Hypothesis (H A ) : The population means of the test scores for the two groups are unequal (μ 1 ≠ μ 2 ).
Choosing the correct hypothesis test depends on attributes such as data type and number of groups. Because they’re using continuous data and comparing two means, the researchers use a 2-sample t-test .
Here are the results.

The treatment group’s mean is 58.70, compared to the control group’s mean of 48.12. The mean difference is 10.67 points. Use the test’s p-value and significance level to determine whether this difference is likely a product of random fluctuation in the sample or a genuine population effect.
Because the p-value (0.000) is less than the standard significance level of 0.05, the results are statistically significant, and we can reject the null hypothesis. The sample data provides sufficient evidence to conclude that the new program’s effect exists in the population.
Limitations
Hypothesis testing improves your effectiveness in making data-driven decisions. However, it is not 100% accurate because random samples occasionally produce fluky results. Hypothesis tests have two types of errors, both relating to drawing incorrect conclusions.
- Type I error: The test rejects a true null hypothesis—a false positive.
- Type II error: The test fails to reject a false null hypothesis—a false negative.
Learn more about Type I and Type II Errors .
Our exploration of hypothesis testing using a practical example of an educational program reveals its powerful ability to guide decisions based on statistical evidence. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, understanding and applying these procedures can open new doors to discovering insights and making informed decisions. Let this tool empower your analytical endeavors as you navigate through the vast seas of data.
Learn more about the Hypothesis Tests for Various Data Types .
Share this:

Reader Interactions
June 10, 2024 at 10:51 am
Thank you, Jim, for another helpful article; timely too since I have started reading your new book on hypothesis testing and, now that we are at the end of the school year, my district is asking me to perform a number of evaluations on instructional programs. This is where my question/concern comes in. You mention that hypothesis testing is all about testing samples. However, I use all the students in my district when I make these comparisons. Since I am using the entire “population” in my evaluations (I don’t select a sample of third grade students, for example, but I use all 700 third graders), am I somehow misusing the tests? Or can I rest assured that my district’s student population is only a sample of the universal population of students?
June 10, 2024 at 1:50 pm
I hope you are finding the book helpful!
Yes, the purpose of hypothesis testing is to infer the properties of a population while accounting for random sampling error.
In your case, it comes down to how you want to use the results. Who do you want the results to apply to?
If you’re summarizing the sample, looking for trends and patterns, or evaluating those students and don’t plan to apply those results to other students, you don’t need hypothesis testing because there is no sampling error. They are the population and you can just use descriptive statistics. In this case, you’d only need to focus on the practical significance of the effect sizes.
On the other hand, if you want to apply the results from this group to other students, you’ll need hypothesis testing. However, there is the complicating issue of what population your sample of students represent. I’m sure your district has its own unique characteristics, demographics, etc. Your district’s students probably don’t adequately represent a universal population. At the very least, you’d need to recognize any special attributes of your district and how they could bias the results when trying to apply them outside the district. Or they might apply to similar districts in your region.
However, I’d imagine your 3rd graders probably adequately represent future classes of 3rd graders in your district. You need to be alert to changing demographics. At least in the short run I’d imagine they’d be representative of future classes.
Think about how these results will be used. Do they just apply to the students you measured? Then you don’t need hypothesis tests. However, if the results are being used to infer things about other students outside of the sample, you’ll need hypothesis testing along with considering how well your students represent the other students and how they differ.
I hope that helps!
June 10, 2024 at 3:21 pm
Thank you so much, Jim, for the suggestions in terms of what I need to think about and consider! You are always so clear in your explanations!!!!
June 10, 2024 at 3:22 pm
You’re very welcome! Best of luck with your evaluations!
Comments and Questions Cancel reply

How to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
The story of a research study begins by asking a question. Researchers all around the globe are asking curious questions and formulating research hypothesis. However, whether the research study provides an effective conclusion depends on how well one develops a good research hypothesis. Research hypothesis examples could help researchers get an idea as to how to write a good research hypothesis.
This blog will help you understand what is a research hypothesis, its characteristics and, how to formulate a research hypothesis
Table of Contents
What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is an assumption or an idea proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested. It is a precise, testable statement of what the researchers predict will be outcome of the study. Hypothesis usually involves proposing a relationship between two variables: the independent variable (what the researchers change) and the dependent variable (what the research measures).
What is a Research Hypothesis?
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It is an integral part of the scientific method that forms the basis of scientific experiments. Therefore, you need to be careful and thorough when building your research hypothesis. A minor flaw in the construction of your hypothesis could have an adverse effect on your experiment. In research, there is a convention that the hypothesis is written in two forms, the null hypothesis, and the alternative hypothesis (called the experimental hypothesis when the method of investigation is an experiment).
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
As the hypothesis is specific, there is a testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. You may consider drawing hypothesis from previously published research based on the theory.
A good research hypothesis involves more effort than just a guess. In particular, your hypothesis may begin with a question that could be further explored through background research.
To help you formulate a promising research hypothesis, you should ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the language clear and focused?
- What is the relationship between your hypothesis and your research topic?
- Is your hypothesis testable? If yes, then how?
- What are the possible explanations that you might want to explore?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate your variables without hampering the ethical standards?
- Does your research predict the relationship and outcome?
- Is your research simple and concise (avoids wordiness)?
- Is it clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Is your research observable and testable results?
- Is it relevant and specific to the research question or problem?

The questions listed above can be used as a checklist to make sure your hypothesis is based on a solid foundation. Furthermore, it can help you identify weaknesses in your hypothesis and revise it if necessary.
Source: Educational Hub
How to formulate a research hypothesis.
A testable hypothesis is not a simple statement. It is rather an intricate statement that needs to offer a clear introduction to a scientific experiment, its intentions, and the possible outcomes. However, there are some important things to consider when building a compelling hypothesis.
1. State the problem that you are trying to solve.
Make sure that the hypothesis clearly defines the topic and the focus of the experiment.
2. Try to write the hypothesis as an if-then statement.
Follow this template: If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.
3. Define the variables
Independent variables are the ones that are manipulated, controlled, or changed. Independent variables are isolated from other factors of the study.
Dependent variables , as the name suggests are dependent on other factors of the study. They are influenced by the change in independent variable.
4. Scrutinize the hypothesis
Evaluate assumptions, predictions, and evidence rigorously to refine your understanding.
Types of Research Hypothesis
The types of research hypothesis are stated below:
1. Simple Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable.
2. Complex Hypothesis
It predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables.
3. Directional Hypothesis
It specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables and is derived from theory. Furthermore, it implies the researcher’s intellectual commitment to a particular outcome.
4. Non-directional Hypothesis
It does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. The non-directional hypothesis is used when there is no theory involved or when findings contradict previous research.
5. Associative and Causal Hypothesis
The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables. A change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. On the other hand, the causal hypothesis proposes an effect on the dependent due to manipulation of the independent variable.
6. Null Hypothesis
Null hypothesis states a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. There will be no changes in the dependent variable due the manipulation of the independent variable. Furthermore, it states results are due to chance and are not significant in terms of supporting the idea being investigated.
7. Alternative Hypothesis
It states that there is a relationship between the two variables of the study and that the results are significant to the research topic. An experimental hypothesis predicts what changes will take place in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated. Also, it states that the results are not due to chance and that they are significant in terms of supporting the theory being investigated.
Research Hypothesis Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
Research Hypothesis Example 1 The greater number of coal plants in a region (independent variable) increases water pollution (dependent variable). If you change the independent variable (building more coal factories), it will change the dependent variable (amount of water pollution).
Research Hypothesis Example 2 What is the effect of diet or regular soda (independent variable) on blood sugar levels (dependent variable)? If you change the independent variable (the type of soda you consume), it will change the dependent variable (blood sugar levels)
You should not ignore the importance of the above steps. The validity of your experiment and its results rely on a robust testable hypothesis. Developing a strong testable hypothesis has few advantages, it compels us to think intensely and specifically about the outcomes of a study. Consequently, it enables us to understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved in the study. Furthermore, it helps us to make precise predictions based on prior research. Hence, forming a hypothesis would be of great value to the research. Here are some good examples of testable hypotheses.
More importantly, you need to build a robust testable research hypothesis for your scientific experiments. A testable hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved as a result of experimentation.
Importance of a Testable Hypothesis
To devise and perform an experiment using scientific method, you need to make sure that your hypothesis is testable. To be considered testable, some essential criteria must be met:
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is true.
- There must be a possibility to prove that the hypothesis is false.
- The results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.
Without these criteria, the hypothesis and the results will be vague. As a result, the experiment will not prove or disprove anything significant.
What are your experiences with building hypotheses for scientific experiments? What challenges did you face? How did you overcome these challenges? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section.
Frequently Asked Questions
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a ‘if-then’ structure. 3. Defining the variables: Define the variables as Dependent or Independent based on their dependency to other factors. 4. Scrutinizing the hypothesis: Identify the type of your hypothesis
Hypothesis testing is a statistical tool which is used to make inferences about a population data to draw conclusions for a particular hypothesis.
Hypothesis in statistics is a formal statement about the nature of a population within a structured framework of a statistical model. It is used to test an existing hypothesis by studying a population.
Research hypothesis is a statement that introduces a research question and proposes an expected result. It forms the basis of scientific experiments.
The different types of hypothesis in research are: • Null hypothesis: Null hypothesis is a negative statement to support the researcher’s findings that there is no relationship between two variables. • Alternate hypothesis: Alternate hypothesis predicts the relationship between the two variables of the study. • Directional hypothesis: Directional hypothesis specifies the expected direction to be followed to determine the relationship between variables. • Non-directional hypothesis: Non-directional hypothesis does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables. • Simple hypothesis: Simple hypothesis predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable. • Complex hypothesis: Complex hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Associative and casual hypothesis: Associative and casual hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. • Empirical hypothesis: Empirical hypothesis can be tested via experiments and observation. • Statistical hypothesis: A statistical hypothesis utilizes statistical models to draw conclusions about broader populations.
Wow! You really simplified your explanation that even dummies would find it easy to comprehend. Thank you so much.
Thanks a lot for your valuable guidance.
I enjoy reading the post. Hypotheses are actually an intrinsic part in a study. It bridges the research question and the methodology of the study.
Useful piece!
This is awesome.Wow.
It very interesting to read the topic, can you guide me any specific example of hypothesis process establish throw the Demand and supply of the specific product in market
Nicely explained
It is really a useful for me Kindly give some examples of hypothesis
It was a well explained content ,can you please give me an example with the null and alternative hypothesis illustrated
clear and concise. thanks.
So Good so Amazing
Good to learn
Thanks a lot for explaining to my level of understanding
Explained well and in simple terms. Quick read! Thank you
It awesome. It has really positioned me in my research project
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Industry News
COPE Forum Discussion Highlights Challenges and Urges Clarity in Institutional Authorship Standards
The COPE forum discussion held in December 2023 initiated with a fundamental question — is…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What would be most effective in reducing research misconduct?

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.3: The Research Hypothesis and the Null Hypothesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 18038

- Michelle Oja
- Taft College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Hypotheses are predictions of expected findings.
The Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a mathematical way of stating a research question. A research hypothesis names the groups (we'll start with a sample and a population), what was measured, and which we think will have a higher mean. The last one gives the research hypothesis a direction. In other words, a research hypothesis should include:
- The name of the groups being compared. This is sometimes considered the IV.
- What was measured. This is the DV.
- Which group are we predicting will have the higher mean.
There are two types of research hypotheses related to sample means and population means: Directional Research Hypotheses and Non-Directional Research Hypotheses
Directional Research Hypothesis
If we expect our obtained sample mean to be above or below the other group's mean (the population mean, for example), we have a directional hypothesis. There are two options:
- Symbol: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} > \mu \)
- (The mean of the sample is greater than than the mean of the population.)
- Symbol: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} < \mu \)
- (The mean of the sample is less than than mean of the population.)
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A study by Blackwell, Trzesniewski, and Dweck (2007) measured growth mindset and how long the junior high student participants spent on their math homework. What’s a directional hypothesis for how scoring higher on growth mindset (compared to the population of junior high students) would be related to how long students spent on their homework? Write this out in words and symbols.
Answer in Words: Students who scored high on growth mindset would spend more time on their homework than the population of junior high students.
Answer in Symbols: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} > \mu \)
Non-Directional Research Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis states that the means will be different, but does not specify which will be higher. In reality, there is rarely a situation in which we actually don't want one group to be higher than the other, so we will focus on directional research hypotheses. There is only one option for a non-directional research hypothesis: "The sample mean differs from the population mean." These types of research hypotheses don’t give a direction, the hypothesis doesn’t say which will be higher or lower.
A non-directional research hypothesis in symbols should look like this: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} \neq \mu \) (The mean of the sample is not equal to the mean of the population).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
What’s a non-directional hypothesis for how scoring higher on growth mindset higher on growth mindset (compared to the population of junior high students) would be related to how long students spent on their homework (Blackwell, Trzesniewski, & Dweck, 2007)? Write this out in words and symbols.
Answer in Words: Students who scored high on growth mindset would spend a different amount of time on their homework than the population of junior high students.
Answer in Symbols: \( \displaystyle \bar{X} \neq \mu \)
See how a non-directional research hypothesis doesn't really make sense? The big issue is not if the two groups differ, but if one group seems to improve what was measured (if having a growth mindset leads to more time spent on math homework). This textbook will only use directional research hypotheses because researchers almost always have a predicted direction (meaning that we almost always know which group we think will score higher).
The Null Hypothesis
The hypothesis that an apparent effect is due to chance is called the null hypothesis, written \(H_0\) (“H-naught”). We usually test this through comparing an experimental group to a comparison (control) group. This null hypothesis can be written as:
\[\mathrm{H}_{0}: \bar{X} = \mu \nonumber \]
For most of this textbook, the null hypothesis is that the means of the two groups are similar. Much later, the null hypothesis will be that there is no relationship between the two groups. Either way, remember that a null hypothesis is always saying that nothing is different.
This is where descriptive statistics diverge from inferential statistics. We know what the value of \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\) is – it’s not a mystery or a question, it is what we observed from the sample. What we are using inferential statistics to do is infer whether this sample's descriptive statistics probably represents the population's descriptive statistics. This is the null hypothesis, that the two groups are similar.
Keep in mind that the null hypothesis is typically the opposite of the research hypothesis. A research hypothesis for the ESP example is that those in my sample who say that they have ESP would get more correct answers than the population would get correct, while the null hypothesis is that the average number correct for the two groups will be similar.
In general, the null hypothesis is the idea that nothing is going on: there is no effect of our treatment, no relation between our variables, and no difference in our sample mean from what we expected about the population mean. This is always our baseline starting assumption, and it is what we seek to reject. If we are trying to treat depression, we want to find a difference in average symptoms between our treatment and control groups. If we are trying to predict job performance, we want to find a relation between conscientiousness and evaluation scores. However, until we have evidence against it, we must use the null hypothesis as our starting point.
In sum, the null hypothesis is always : There is no difference between the groups’ means OR There is no relationship between the variables .
In the next chapter, the null hypothesis is that there’s no difference between the sample mean and population mean. In other words:
- There is no mean difference between the sample and population.
- The mean of the sample is the same as the mean of a specific population.
- \(\mathrm{H}_{0}: \bar{X} = \mu \nonumber \)
- We expect our sample’s mean to be same as the population mean.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
A study by Blackwell, Trzesniewski, and Dweck (2007) measured growth mindset and how long the junior high student participants spent on their math homework. What’s the null hypothesis for scoring higher on growth mindset (compared to the population of junior high students) and how long students spent on their homework? Write this out in words and symbols.
Answer in Words: Students who scored high on growth mindset would spend a similar amount of time on their homework as the population of junior high students.
Answer in Symbols: \( \bar{X} = \mu \)
Contributors and Attributions
Foster et al. (University of Missouri-St. Louis, Rice University, & University of Houston, Downtown Campus)
Dr. MO ( Taft College )
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.53(4); 2010 Aug

Research questions, hypotheses and objectives
Patricia farrugia.
* Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine, the
Bradley A. Petrisor
† Division of Orthopaedic Surgery and the
Forough Farrokhyar
‡ Departments of Surgery and
§ Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont
Mohit Bhandari
There is an increasing familiarity with the principles of evidence-based medicine in the surgical community. As surgeons become more aware of the hierarchy of evidence, grades of recommendations and the principles of critical appraisal, they develop an increasing familiarity with research design. Surgeons and clinicians are looking more and more to the literature and clinical trials to guide their practice; as such, it is becoming a responsibility of the clinical research community to attempt to answer questions that are not only well thought out but also clinically relevant. The development of the research question, including a supportive hypothesis and objectives, is a necessary key step in producing clinically relevant results to be used in evidence-based practice. A well-defined and specific research question is more likely to help guide us in making decisions about study design and population and subsequently what data will be collected and analyzed. 1
Objectives of this article
In this article, we discuss important considerations in the development of a research question and hypothesis and in defining objectives for research. By the end of this article, the reader will be able to appreciate the significance of constructing a good research question and developing hypotheses and research objectives for the successful design of a research study. The following article is divided into 3 sections: research question, research hypothesis and research objectives.
Research question
Interest in a particular topic usually begins the research process, but it is the familiarity with the subject that helps define an appropriate research question for a study. 1 Questions then arise out of a perceived knowledge deficit within a subject area or field of study. 2 Indeed, Haynes suggests that it is important to know “where the boundary between current knowledge and ignorance lies.” 1 The challenge in developing an appropriate research question is in determining which clinical uncertainties could or should be studied and also rationalizing the need for their investigation.
Increasing one’s knowledge about the subject of interest can be accomplished in many ways. Appropriate methods include systematically searching the literature, in-depth interviews and focus groups with patients (and proxies) and interviews with experts in the field. In addition, awareness of current trends and technological advances can assist with the development of research questions. 2 It is imperative to understand what has been studied about a topic to date in order to further the knowledge that has been previously gathered on a topic. Indeed, some granting institutions (e.g., Canadian Institute for Health Research) encourage applicants to conduct a systematic review of the available evidence if a recent review does not already exist and preferably a pilot or feasibility study before applying for a grant for a full trial.
In-depth knowledge about a subject may generate a number of questions. It then becomes necessary to ask whether these questions can be answered through one study or if more than one study needed. 1 Additional research questions can be developed, but several basic principles should be taken into consideration. 1 All questions, primary and secondary, should be developed at the beginning and planning stages of a study. Any additional questions should never compromise the primary question because it is the primary research question that forms the basis of the hypothesis and study objectives. It must be kept in mind that within the scope of one study, the presence of a number of research questions will affect and potentially increase the complexity of both the study design and subsequent statistical analyses, not to mention the actual feasibility of answering every question. 1 A sensible strategy is to establish a single primary research question around which to focus the study plan. 3 In a study, the primary research question should be clearly stated at the end of the introduction of the grant proposal, and it usually specifies the population to be studied, the intervention to be implemented and other circumstantial factors. 4
Hulley and colleagues 2 have suggested the use of the FINER criteria in the development of a good research question ( Box 1 ). The FINER criteria highlight useful points that may increase the chances of developing a successful research project. A good research question should specify the population of interest, be of interest to the scientific community and potentially to the public, have clinical relevance and further current knowledge in the field (and of course be compliant with the standards of ethical boards and national research standards).
FINER criteria for a good research question
| Feasible | ||
| Interesting | ||
| Novel | ||
| Ethical | ||
| Relevant |
Adapted with permission from Wolters Kluwer Health. 2
Whereas the FINER criteria outline the important aspects of the question in general, a useful format to use in the development of a specific research question is the PICO format — consider the population (P) of interest, the intervention (I) being studied, the comparison (C) group (or to what is the intervention being compared) and the outcome of interest (O). 3 , 5 , 6 Often timing (T) is added to PICO ( Box 2 ) — that is, “Over what time frame will the study take place?” 1 The PICOT approach helps generate a question that aids in constructing the framework of the study and subsequently in protocol development by alluding to the inclusion and exclusion criteria and identifying the groups of patients to be included. Knowing the specific population of interest, intervention (and comparator) and outcome of interest may also help the researcher identify an appropriate outcome measurement tool. 7 The more defined the population of interest, and thus the more stringent the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the greater the effect on the interpretation and subsequent applicability and generalizability of the research findings. 1 , 2 A restricted study population (and exclusion criteria) may limit bias and increase the internal validity of the study; however, this approach will limit external validity of the study and, thus, the generalizability of the findings to the practical clinical setting. Conversely, a broadly defined study population and inclusion criteria may be representative of practical clinical practice but may increase bias and reduce the internal validity of the study.
PICOT criteria 1
| Population (patients) | ||
| Intervention (for intervention studies only) | ||
| Comparison group | ||
| Outcome of interest | ||
| Time |
A poorly devised research question may affect the choice of study design, potentially lead to futile situations and, thus, hamper the chance of determining anything of clinical significance, which will then affect the potential for publication. Without devoting appropriate resources to developing the research question, the quality of the study and subsequent results may be compromised. During the initial stages of any research study, it is therefore imperative to formulate a research question that is both clinically relevant and answerable.
Research hypothesis
The primary research question should be driven by the hypothesis rather than the data. 1 , 2 That is, the research question and hypothesis should be developed before the start of the study. This sounds intuitive; however, if we take, for example, a database of information, it is potentially possible to perform multiple statistical comparisons of groups within the database to find a statistically significant association. This could then lead one to work backward from the data and develop the “question.” This is counterintuitive to the process because the question is asked specifically to then find the answer, thus collecting data along the way (i.e., in a prospective manner). Multiple statistical testing of associations from data previously collected could potentially lead to spuriously positive findings of association through chance alone. 2 Therefore, a good hypothesis must be based on a good research question at the start of a trial and, indeed, drive data collection for the study.
The research or clinical hypothesis is developed from the research question and then the main elements of the study — sampling strategy, intervention (if applicable), comparison and outcome variables — are summarized in a form that establishes the basis for testing, statistical and ultimately clinical significance. 3 For example, in a research study comparing computer-assisted acetabular component insertion versus freehand acetabular component placement in patients in need of total hip arthroplasty, the experimental group would be computer-assisted insertion and the control/conventional group would be free-hand placement. The investigative team would first state a research hypothesis. This could be expressed as a single outcome (e.g., computer-assisted acetabular component placement leads to improved functional outcome) or potentially as a complex/composite outcome; that is, more than one outcome (e.g., computer-assisted acetabular component placement leads to both improved radiographic cup placement and improved functional outcome).
However, when formally testing statistical significance, the hypothesis should be stated as a “null” hypothesis. 2 The purpose of hypothesis testing is to make an inference about the population of interest on the basis of a random sample taken from that population. The null hypothesis for the preceding research hypothesis then would be that there is no difference in mean functional outcome between the computer-assisted insertion and free-hand placement techniques. After forming the null hypothesis, the researchers would form an alternate hypothesis stating the nature of the difference, if it should appear. The alternate hypothesis would be that there is a difference in mean functional outcome between these techniques. At the end of the study, the null hypothesis is then tested statistically. If the findings of the study are not statistically significant (i.e., there is no difference in functional outcome between the groups in a statistical sense), we cannot reject the null hypothesis, whereas if the findings were significant, we can reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate hypothesis (i.e., there is a difference in mean functional outcome between the study groups), errors in testing notwithstanding. In other words, hypothesis testing confirms or refutes the statement that the observed findings did not occur by chance alone but rather occurred because there was a true difference in outcomes between these surgical procedures. The concept of statistical hypothesis testing is complex, and the details are beyond the scope of this article.
Another important concept inherent in hypothesis testing is whether the hypotheses will be 1-sided or 2-sided. A 2-sided hypothesis states that there is a difference between the experimental group and the control group, but it does not specify in advance the expected direction of the difference. For example, we asked whether there is there an improvement in outcomes with computer-assisted surgery or whether the outcomes worse with computer-assisted surgery. We presented a 2-sided test in the above example because we did not specify the direction of the difference. A 1-sided hypothesis states a specific direction (e.g., there is an improvement in outcomes with computer-assisted surgery). A 2-sided hypothesis should be used unless there is a good justification for using a 1-sided hypothesis. As Bland and Atlman 8 stated, “One-sided hypothesis testing should never be used as a device to make a conventionally nonsignificant difference significant.”
The research hypothesis should be stated at the beginning of the study to guide the objectives for research. Whereas the investigators may state the hypothesis as being 1-sided (there is an improvement with treatment), the study and investigators must adhere to the concept of clinical equipoise. According to this principle, a clinical (or surgical) trial is ethical only if the expert community is uncertain about the relative therapeutic merits of the experimental and control groups being evaluated. 9 It means there must exist an honest and professional disagreement among expert clinicians about the preferred treatment. 9
Designing a research hypothesis is supported by a good research question and will influence the type of research design for the study. Acting on the principles of appropriate hypothesis development, the study can then confidently proceed to the development of the research objective.
Research objective
The primary objective should be coupled with the hypothesis of the study. Study objectives define the specific aims of the study and should be clearly stated in the introduction of the research protocol. 7 From our previous example and using the investigative hypothesis that there is a difference in functional outcomes between computer-assisted acetabular component placement and free-hand placement, the primary objective can be stated as follows: this study will compare the functional outcomes of computer-assisted acetabular component insertion versus free-hand placement in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Note that the study objective is an active statement about how the study is going to answer the specific research question. Objectives can (and often do) state exactly which outcome measures are going to be used within their statements. They are important because they not only help guide the development of the protocol and design of study but also play a role in sample size calculations and determining the power of the study. 7 These concepts will be discussed in other articles in this series.
From the surgeon’s point of view, it is important for the study objectives to be focused on outcomes that are important to patients and clinically relevant. For example, the most methodologically sound randomized controlled trial comparing 2 techniques of distal radial fixation would have little or no clinical impact if the primary objective was to determine the effect of treatment A as compared to treatment B on intraoperative fluoroscopy time. However, if the objective was to determine the effect of treatment A as compared to treatment B on patient functional outcome at 1 year, this would have a much more significant impact on clinical decision-making. Second, more meaningful surgeon–patient discussions could ensue, incorporating patient values and preferences with the results from this study. 6 , 7 It is the precise objective and what the investigator is trying to measure that is of clinical relevance in the practical setting.
The following is an example from the literature about the relation between the research question, hypothesis and study objectives:
Study: Warden SJ, Metcalf BR, Kiss ZS, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for chronic patellar tendinopathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatology 2008;47:467–71.
Research question: How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
Research hypothesis: Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
Objective: To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
The development of the research question is the most important aspect of a research project. A research project can fail if the objectives and hypothesis are poorly focused and underdeveloped. Useful tips for surgical researchers are provided in Box 3 . Designing and developing an appropriate and relevant research question, hypothesis and objectives can be a difficult task. The critical appraisal of the research question used in a study is vital to the application of the findings to clinical practice. Focusing resources, time and dedication to these 3 very important tasks will help to guide a successful research project, influence interpretation of the results and affect future publication efforts.
Tips for developing research questions, hypotheses and objectives for research studies
- Perform a systematic literature review (if one has not been done) to increase knowledge and familiarity with the topic and to assist with research development.
- Learn about current trends and technological advances on the topic.
- Seek careful input from experts, mentors, colleagues and collaborators to refine your research question as this will aid in developing the research question and guide the research study.
- Use the FINER criteria in the development of the research question.
- Ensure that the research question follows PICOT format.
- Develop a research hypothesis from the research question.
- Develop clear and well-defined primary and secondary (if needed) objectives.
- Ensure that the research question and objectives are answerable, feasible and clinically relevant.
FINER = feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, relevant; PICOT = population (patients), intervention (for intervention studies only), comparison group, outcome of interest, time.
Competing interests: No funding was received in preparation of this paper. Dr. Bhandari was funded, in part, by a Canada Research Chair, McMaster University.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples
Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on June 22, 2023.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test :
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): There’s no effect in the population .
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a or H 1 ) : There’s an effect in the population.
Table of contents
Answering your research question with hypotheses, what is a null hypothesis, what is an alternative hypothesis, similarities and differences between null and alternative hypotheses, how to write null and alternative hypotheses, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question . When the research question asks “Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?”:
- The null hypothesis ( H 0 ) answers “No, there’s no effect in the population.”
- The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) answers “Yes, there is an effect in the population.”
The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That’s because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample . Often, we infer whether there’s an effect in the population by looking at differences between groups or relationships between variables in the sample. It’s critical for your research to write strong hypotheses .
You can use a statistical test to decide whether the evidence favors the null or alternative hypothesis. Each type of statistical test comes with a specific way of phrasing the null and alternative hypothesis. However, the hypotheses can also be phrased in a general way that applies to any test.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The null hypothesis is the claim that there’s no effect in the population.
If the sample provides enough evidence against the claim that there’s no effect in the population ( p ≤ α), then we can reject the null hypothesis . Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Although “fail to reject” may sound awkward, it’s the only wording that statisticians accept . Be careful not to say you “prove” or “accept” the null hypothesis.
Null hypotheses often include phrases such as “no effect,” “no difference,” or “no relationship.” When written in mathematical terms, they always include an equality (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
You can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population. Some percentage of the time, your inference about the population will be incorrect. When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error . When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s a type II error.
Examples of null hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and null hypotheses. There’s always more than one way to answer a research question, but these null hypotheses can help you get started.
| ( ) | ||
| Does tooth flossing affect the number of cavities? | Tooth flossing has on the number of cavities. | test: The mean number of cavities per person does not differ between the flossing group (µ ) and the non-flossing group (µ ) in the population; µ = µ . |
| Does the amount of text highlighted in the textbook affect exam scores? | The amount of text highlighted in the textbook has on exam scores. | : There is no relationship between the amount of text highlighted and exam scores in the population; β = 0. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation the incidence of depression.* | test: The proportion of people with depression in the daily-meditation group ( ) is greater than or equal to the no-meditation group ( ) in the population; ≥ . |
*Note that some researchers prefer to always write the null hypothesis in terms of “no effect” and “=”. It would be fine to say that daily meditation has no effect on the incidence of depression and p 1 = p 2 .
The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) is the other answer to your research question . It claims that there’s an effect in the population.
Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it’s the claim that you expect or hope will be true.
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. Null and alternative hypotheses are exhaustive, meaning that together they cover every possible outcome. They are also mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
Alternative hypotheses often include phrases such as “an effect,” “a difference,” or “a relationship.” When alternative hypotheses are written in mathematical terms, they always include an inequality (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >). As with null hypotheses, there are many acceptable ways to phrase an alternative hypothesis.
Examples of alternative hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and alternative hypotheses to help you get started with formulating your own.
| Does tooth flossing affect the number of cavities? | Tooth flossing has an on the number of cavities. | test: The mean number of cavities per person differs between the flossing group (µ ) and the non-flossing group (µ ) in the population; µ ≠ µ . |
| Does the amount of text highlighted in a textbook affect exam scores? | The amount of text highlighted in the textbook has an on exam scores. | : There is a relationship between the amount of text highlighted and exam scores in the population; β ≠ 0. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation the incidence of depression. | test: The proportion of people with depression in the daily-meditation group ( ) is less than the no-meditation group ( ) in the population; < . |
Null and alternative hypotheses are similar in some ways:
- They’re both answers to the research question.
- They both make claims about the population.
- They’re both evaluated by statistical tests.
However, there are important differences between the two types of hypotheses, summarized in the following table.
| A claim that there is in the population. | A claim that there is in the population. | |
|
| ||
| Equality symbol (=, ≥, or ≤) | Inequality symbol (≠, <, or >) | |
| Rejected | Supported | |
| Failed to reject | Not supported |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To help you write your hypotheses, you can use the template sentences below. If you know which statistical test you’re going to use, you can use the test-specific template sentences. Otherwise, you can use the general template sentences.
General template sentences
The only thing you need to know to use these general template sentences are your dependent and independent variables. To write your research question, null hypothesis, and alternative hypothesis, fill in the following sentences with your variables:
Does independent variable affect dependent variable ?
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): Independent variable does not affect dependent variable.
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a ): Independent variable affects dependent variable.
Test-specific template sentences
Once you know the statistical test you’ll be using, you can write your hypotheses in a more precise and mathematical way specific to the test you chose. The table below provides template sentences for common statistical tests.
| ( ) | ||
| test
with two groups | The mean dependent variable does not differ between group 1 (µ ) and group 2 (µ ) in the population; µ = µ . | The mean dependent variable differs between group 1 (µ ) and group 2 (µ ) in the population; µ ≠ µ . |
| with three groups | The mean dependent variable does not differ between group 1 (µ ), group 2 (µ ), and group 3 (µ ) in the population; µ = µ = µ . | The mean dependent variable of group 1 (µ ), group 2 (µ ), and group 3 (µ ) are not all equal in the population. |
| There is no correlation between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; ρ = 0. | There is a correlation between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; ρ ≠ 0. | |
| There is no relationship between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; β = 0. | There is a relationship between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; β ≠ 0. | |
| Two-proportions test | The dependent variable expressed as a proportion does not differ between group 1 ( ) and group 2 ( ) in the population; = . | The dependent variable expressed as a proportion differs between group 1 ( ) and group 2 ( ) in the population; ≠ . |
Note: The template sentences above assume that you’re performing one-tailed tests . One-tailed tests are appropriate for most studies.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
The null hypothesis is often abbreviated as H 0 . When the null hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an equality symbol (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
The alternative hypothesis is often abbreviated as H a or H 1 . When the alternative hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an inequality symbol (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Turney, S. (2023, June 22). Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/null-and-alternative-hypotheses/
Is this article helpful?

Shaun Turney
Other students also liked, inferential statistics | an easy introduction & examples, hypothesis testing | a step-by-step guide with easy examples, type i & type ii errors | differences, examples, visualizations, what is your plagiarism score.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Hypothesis Vs Null Hypothesis
Research Hypothesis Vs Null Hypothesis
Table of Contents

The difference between Research Hypothesis Vs Null Hypothesis is as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A Research Hypothesis is a tentative statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. It is based on a theoretical or conceptual framework and is typically tested through empirical research.
Null Hypothesis
A Null Hypothesis is a statement that proposes that there is no relationship between two or more variables. It is the opposite of the research hypothesis and is used as a comparison in statistical analysis.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Research Hypothesis | Null Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tentative statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables | Statement that proposes no relationship between two or more variables |
| Purpose | To guide research and provide a framework for testing the relationship between variables | To provide a comparison for the research hypothesis in statistical analysis |
| Format | Expressed in a declarative sentence that describes the expected direction and strength of the relationship between variables | Expressed in a declarative sentence that proposes no effect or relationship between variables |
| Testing | Tested through empirical research | Tested against the research hypothesis in statistical analysis |
| Conclusion | Supported if statistical analysis provides evidence to reject the null hypothesis | Rejected if statistical analysis provides evidence to support the research hypothesis |
| Example | “There is a positive relationship between physical exercise and mental health.” | “There is no relationship between physical exercise and mental health.” |
In summary, a research hypothesis proposes a relationship between variables, while a null hypothesis proposes no relationship between variables. The research hypothesis guides empirical research, while the null hypothesis is used as a comparison in statistical analysis. The research hypothesis is supported if statistical analysis provides evidence to reject the null hypothesis, while the null hypothesis is rejected if statistical analysis provides evidence to support the research hypothesis.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Qualitative Vs Quantitative Research

Exploratory Vs Explanatory Research

Descriptive vs Experimental Research

Longitudinal Vs Cross-Sectional Research

Correlational Research Vs Experimental Research

Basic Vs Applied Research

What is Hypothesis? Definition, Meaning, Characteristics, Sources
- Post last modified: 10 January 2022
- Reading time: 18 mins read
- Post category: Research Methodology

- What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
As an example, if we want to explore whether using a specific teaching method at school will result in better school marks (research question), the hypothesis could be that the mean school marks of students being taught with that specific teaching method will be higher than of those being taught using other methods.
In this example, we stated a hypothesis about the expected differences between groups. Other hypotheses may refer to correlations between variables.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Hypothesis?
- 2 Hypothesis Definition
- 3 Meaning of Hypothesis
- 4.1 Conceptual Clarity
- 4.2 Need of empirical referents
- 4.3 Hypothesis should be specific
- 4.4 Hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques
- 4.5 Hypothesis should be consistent with the theory
- 4.6 Hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events
- 4.7 Hypothesis should be simple
- 5.1 Observation
- 5.2 Analogies
- 5.4 State of Knowledge
- 5.5 Culture
- 5.6 Continuity of Research
- 6.1 Null Hypothesis
- 6.2 Alternative Hypothesis
Thus, to formulate a hypothesis, we need to refer to the descriptive statistics (such as the mean final marks), and specify a set of conditions about these statistics (such as a difference between the means, or in a different example, a positive or negative correlation). The hypothesis we formulate applies to the population of interest.
The null hypothesis makes a statement that no difference exists (see Pyrczak, 1995, pp. 75-84).
Hypothesis Definition
A hypothesis is ‘a guess or supposition as to the existence of some fact or law which will serve to explain a connection of facts already known to exist.’ – J. E. Creighton & H. R. Smart
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition not known to be definitely true or false, examined for the sake of determining the consequences which would follow from its truth.’ – Max Black
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition which can be put to a test to determine validity and is useful for further research.’ – W. J. Goode and P. K. Hatt
A hypothesis is a proposition, condition or principle which is assumed, perhaps without belief, in order to draw out its logical consequences and by this method to test its accord with facts which are known or may be determined. – Webster’s New International Dictionary of the English Language (1956)
Meaning of Hypothesis
From the above mentioned definitions of hypothesis, its meaning can be explained in the following ways.
- At the primary level, a hypothesis is the possible and probable explanation of the sequence of happenings or data.
- Sometimes, hypothesis may emerge from an imagination, common sense or a sudden event.
- Hypothesis can be a probable answer to the research problem undertaken for study. 4. Hypothesis may not always be true. It can get disproven. In other words, hypothesis need not always be a true proposition.
- Hypothesis, in a sense, is an attempt to present the interrelations that exist in the available data or information.
- Hypothesis is not an individual opinion or community thought. Instead, it is a philosophical means which is to be used for research purpose. Hypothesis is not to be considered as the ultimate objective; rather it is to be taken as the means of explaining scientifically the prevailing situation.
The concept of hypothesis can further be explained with the help of some examples. Lord Keynes, in his theory of national income determination, made a hypothesis about the consumption function. He stated that the consumption expenditure of an individual or an economy as a whole is dependent on the level of income and changes in a certain proportion.
Later, this proposition was proved in the statistical research carried out by Prof. Simon Kuznets. Matthus, while studying the population, formulated a hypothesis that population increases faster than the supply of food grains. Population studies of several countries revealed that this hypothesis is true.
Validation of the Malthus’ hypothesis turned it into a theory and when it was tested in many other countries it became the famous Malthus’ Law of Population. It thus emerges that when a hypothesis is tested and proven, it becomes a theory. The theory, when found true in different times and at different places, becomes the law. Having understood the concept of hypothesis, few hypotheses can be formulated in the areas of commerce and economics.
- Population growth moderates with the rise in per capita income.
- Sales growth is positively linked with the availability of credit.
- Commerce education increases the employability of the graduate students.
- High rates of direct taxes prompt people to evade taxes.
- Good working conditions improve the productivity of employees.
- Advertising is the most effecting way of promoting sales than any other scheme.
- Higher Debt-Equity Ratio increases the probability of insolvency.
- Economic reforms in India have made the public sector banks more efficient and competent.
- Foreign direct investment in India has moved in those sectors which offer higher rate of profit.
- There is no significant association between credit rating and investment of fund.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Not all the hypotheses are good and useful from the point of view of research. It is only a few hypotheses satisfying certain criteria that are good, useful and directive in the research work undertaken. The characteristics of such a useful hypothesis can be listed as below:
Conceptual Clarity
Need of empirical referents, hypothesis should be specific, hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques, hypothesis should be consistent with the theory, hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events, hypothesis should be simple.
The concepts used while framing hypothesis should be crystal clear and unambiguous. Such concepts must be clearly defined so that they become lucid and acceptable to everyone. How are the newly developed concepts interrelated and how are they linked with the old one is to be very clear so that the hypothesis framed on their basis also carries the same clarity.
A hypothesis embodying unclear and ambiguous concepts can to a great extent undermine the successful completion of the research work.
A hypothesis can be useful in the research work undertaken only when it has links with some empirical referents. Hypothesis based on moral values and ideals are useless as they cannot be tested. Similarly, hypothesis containing opinions as good and bad or expectation with respect to something are not testable and therefore useless.
For example, ‘current account deficit can be lowered if people change their attitude towards gold’ is a hypothesis encompassing expectation. In case of such a hypothesis, the attitude towards gold is something which cannot clearly be described and therefore a hypothesis which embodies such an unclean thing cannot be tested and proved or disproved. In short, the hypothesis should be linked with some testable referents.
For the successful conduction of research, it is necessary that the hypothesis is specific and presented in a precise manner. Hypothesis which is general, too ambitious and grandiose in scope is not to be made as such hypothesis cannot be easily put to test. A hypothesis is to be based on such concepts which are precise and empirical in nature. A hypothesis should give a clear idea about the indicators which are to be used.
For example, a hypothesis that economic power is increasingly getting concentrated in a few hands in India should enable us to define the concept of economic power. It should be explicated in terms of measurable indicator like income, wealth, etc. Such specificity in the formulation of a hypothesis ensures that the research is practicable and significant.
While framing the hypothesis, the researcher should be aware of the available research techniques and should see that the hypothesis framed is testable on the basis of them. In other words, a hypothesis should be researchable and for this it is important that a due thought has been given to the methods and techniques which can be used to measure the concepts and variables embodied in the hypothesis.
It does not however mean that hypotheses which are not testable with the available techniques of research are not to be made. If the problem is too significant and therefore the hypothesis framed becomes too ambitious and complex, it’s testing becomes possible with the development of new research techniques or the hypothesis itself leads to the development of new research techniques.
A hypothesis must be related to the existing theory or should have a theoretical orientation. The growth of knowledge takes place in the sequence of facts, hypothesis, theory and law or principles. It means the hypothesis should have a correspondence with the existing facts and theory.
If the hypothesis is related to some theory, the research work will enable us to support, modify or refute the existing theory. Theoretical orientation of the hypothesis ensures that it becomes scientifically useful. According to Prof. Goode and Prof. Hatt, research work can contribute to the existing knowledge only when the hypothesis is related with some theory.
This enables us to explain the observed facts and situations and also verify the framed hypothesis. In the words of Prof. Cohen and Prof. Nagel, “hypothesis must be formulated in such a manner that deduction can be made from it and that consequently a decision can be reached as to whether it does or does not explain the facts considered.”
If the research work based on a hypothesis is to be successful, it is necessary that the later is as simple and easy as possible. An ambition of finding out something new may lead the researcher to frame an unrealistic and unclear hypothesis. Such a temptation is to be avoided. Framing a simple, easy and testable hypothesis requires that the researcher is well acquainted with the related concepts.
Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can be derived from various sources. Some of the sources is given below:
Observation
State of knowledge, continuity of research.
Hypotheses can be derived from observation from the observation of price behavior in a market. For example the relationship between the price and demand for an article is hypothesized.
Analogies are another source of useful hypotheses. Julian Huxley has pointed out that casual observations in nature or in the framework of another science may be a fertile source of hypotheses. For example, the hypotheses that similar human types or activities may be found in similar geophysical regions come from plant ecology.
This is one of the main sources of hypotheses. It gives direction to research by stating what is known logical deduction from theory lead to new hypotheses. For example, profit / wealth maximization is considered as the goal of private enterprises. From this assumption various hypotheses are derived’.
An important source of hypotheses is the state of knowledge in any particular science where formal theories exist hypotheses can be deduced. If the hypotheses are rejected theories are scarce hypotheses are generated from conception frameworks.
Another source of hypotheses is the culture on which the researcher was nurtured. Western culture has induced the emergence of sociology as an academic discipline over the past decade, a large part of the hypotheses on American society examined by researchers were connected with violence. This interest is related to the considerable increase in the level of violence in America.
The continuity of research in a field itself constitutes an important source of hypotheses. The rejection of some hypotheses leads to the formulation of new ones capable of explaining dependent variables in subsequent research on the same subject.
Null and Alternative Hypothesis
Null hypothesis.
The hypothesis that are proposed with the intent of receiving a rejection for them are called Null Hypothesis . This requires that we hypothesize the opposite of what is desired to be proved. For example, if we want to show that sales and advertisement expenditure are related, we formulate the null hypothesis that they are not related.
Similarly, if we want to conclude that the new sales training programme is effective, we formulate the null hypothesis that the new training programme is not effective, and if we want to prove that the average wages of skilled workers in town 1 is greater than that of town 2, we formulate the null hypotheses that there is no difference in the average wages of the skilled workers in both the towns.
Since we hypothesize that sales and advertisement are not related, new training programme is not effective and the average wages of skilled workers in both the towns are equal, we call such hypotheses null hypotheses and denote them as H 0 .
Alternative Hypothesis
Rejection of null hypotheses leads to the acceptance of alternative hypothesis . The rejection of null hypothesis indicates that the relationship between variables (e.g., sales and advertisement expenditure) or the difference between means (e.g., wages of skilled workers in town 1 and town 2) or the difference between proportions have statistical significance and the acceptance of the null hypotheses indicates that these differences are due to chance.
As already mentioned, the alternative hypotheses specify that values/relation which the researcher believes hold true. The alternative hypotheses can cover a whole range of values rather than a single point. The alternative hypotheses are denoted by H 1 .
Business Ethics
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Theories of CSR
- Arguments Against CSR
- Business Case for CSR
- Importance of CSR in India
- Drivers of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Developing a CSR Strategy
- Implement CSR Commitments
- CSR Marketplace
- CSR at Workplace
- Environmental CSR
- CSR with Communities and in Supply Chain
- Community Interventions
- CSR Monitoring
- CSR Reporting
- Voluntary Codes in CSR
- What is Corporate Ethics?
Lean Six Sigma
- What is Six Sigma?
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Value and Waste in Lean Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Team
- MAIC Six Sigma
- Six Sigma in Supply Chains
- What is Binomial, Poisson, Normal Distribution?
- What is Sigma Level?
- What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
- What is DMADV in Six Sigma?
- Six Sigma Project Charter
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
- Research Methodology
- What is Research?
- Sampling Method
- Research Methods
- Data Collection in Research
- Methods of Collecting Data
- Application of Business Research
- Levels of Measurement
- What is Sampling?
Hypothesis Testing
- Research Report
- What is Management?
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- What is Controlling?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Staffing?
- Organization Structure
- What is Departmentation?
- Span of Control
- What is Authority?
- Centralization vs Decentralization
- Organizing in Management
- Schools of Management Thought
- Classical Management Approach
- Is Management an Art or Science?
- Who is a Manager?
Operations Research
- What is Operations Research?
- Operation Research Models
- Linear Programming
- Linear Programming Graphic Solution
- Linear Programming Simplex Method
- Linear Programming Artificial Variable Technique
- Duality in Linear Programming
- Transportation Problem Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- Transportation Problem Finding Optimal Solution
- Project Network Analysis with Critical Path Method
- Project Network Analysis Methods
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Simulation in Operation Research
- Replacement Models in Operation Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
- What is Service?
- What is Service Operations Management?
- What is Service Design?
- Service Design Process
- Service Delivery
- What is Service Quality?
- Gap Model of Service Quality
- Juran Trilogy
- Service Performance Measurement
- Service Decoupling
- IT Service Operation
- Service Operations Management in Different Sector
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Supply Chain Planning and Measuring Strategy Performance
- What is Warehousing?
- What is Packaging?
- What is Inventory Management?
- What is Material Handling?
- What is Order Picking?
- Receiving and Dispatch, Processes
- What is Warehouse Design?
- What is Warehousing Costs?
You Might Also Like
Primary data and secondary data, cross-sectional and longitudinal research, types of errors affecting research design, what is scaling techniques types, classifications, techniques, data analysis in research, what is questionnaire design characteristics, types, don’t, what is research types, purpose, characteristics, process, what is causal research advantages, disadvantages, how to perform, what is research problem components, identifying, formulating,, ethics in research, measures of relationship, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal Growth

Development
Hypothesis Maker Online
Looking for a hypothesis maker? This online tool for students will help you formulate a beautiful hypothesis quickly, efficiently, and for free.
Are you looking for an effective hypothesis maker online? Worry no more; try our online tool for students and formulate your hypothesis within no time.
- 🔎 How to Use the Tool?
- ⚗️ What Is a Hypothesis in Science?
👍 What Does a Good Hypothesis Mean?
- 🧭 Steps to Making a Good Hypothesis
🔗 References
📄 hypothesis maker: how to use it.
Our hypothesis maker is a simple and efficient tool you can access online for free.
If you want to create a research hypothesis quickly, you should fill out the research details in the given fields on the hypothesis generator.
Below are the fields you should complete to generate your hypothesis:
- Who or what is your research based on? For instance, the subject can be research group 1.
- What does the subject (research group 1) do?
- What does the subject affect? - This shows the predicted outcome, which is the object.
- Who or what will be compared with research group 1? (research group 2).
Once you fill the in the fields, you can click the ‘Make a hypothesis’ tab and get your results.
⚗️ What Is a Hypothesis in the Scientific Method?
A hypothesis is a statement describing an expectation or prediction of your research through observation.
It is similar to academic speculation and reasoning that discloses the outcome of your scientific test . An effective hypothesis, therefore, should be crafted carefully and with precision.
A good hypothesis should have dependent and independent variables . These variables are the elements you will test in your research method – it can be a concept, an event, or an object as long as it is observable.
You can observe the dependent variables while the independent variables keep changing during the experiment.
In a nutshell, a hypothesis directs and organizes the research methods you will use, forming a large section of research paper writing.
Hypothesis vs. Theory
A hypothesis is a realistic expectation that researchers make before any investigation. It is formulated and tested to prove whether the statement is true. A theory, on the other hand, is a factual principle supported by evidence. Thus, a theory is more fact-backed compared to a hypothesis.
Another difference is that a hypothesis is presented as a single statement , while a theory can be an assortment of things . Hypotheses are based on future possibilities toward a specific projection, but the results are uncertain. Theories are verified with undisputable results because of proper substantiation.
When it comes to data, a hypothesis relies on limited information , while a theory is established on an extensive data set tested on various conditions.
You should observe the stated assumption to prove its accuracy.
Since hypotheses have observable variables, their outcome is usually based on a specific occurrence. Conversely, theories are grounded on a general principle involving multiple experiments and research tests.
This general principle can apply to many specific cases.
The primary purpose of formulating a hypothesis is to present a tentative prediction for researchers to explore further through tests and observations. Theories, in their turn, aim to explain plausible occurrences in the form of a scientific study.
It would help to rely on several criteria to establish a good hypothesis. Below are the parameters you should use to analyze the quality of your hypothesis.
| Testability | You should be able to test the hypothesis to present a true or false outcome after the investigation. Apart from the logical hypothesis, ensure you can test your predictions with . |
|---|---|
| Variables | It should have a dependent and independent variable. Identifying the appropriate variables will help readers comprehend your prediction and what to expect at the conclusion phase. |
| Cause and effect | A good hypothesis should have a cause-and-effect connection. One variable should influence others in some way. It should be written as an “if-then” statement to allow the researcher to make accurate predictions of the investigation results. However, this rule does not apply to a . |
| Clear language | Writing can get complex, especially when complex research terminology is involved. So, ensure your hypothesis has expressed as a brief statement. Avoid being vague because your readers might get confused. Your hypothesis has a direct impact on your entire research paper’s quality. Thus, use simple words that are easy to understand. |
| Ethics | Hypothesis generation should comply with . Don’t formulate hypotheses that contravene taboos or are questionable. Besides, your hypothesis should have correlations to published academic works to look data-based and authoritative. |
🧭 6 Steps to Making a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis becomes way simpler if you follow a tried-and-tested algorithm. Let’s explore how you can formulate a good hypothesis in a few steps:
Step #1: Ask Questions
The first step in hypothesis creation is asking real questions about the surrounding reality.
Why do things happen as they do? What are the causes of some occurrences?
Your curiosity will trigger great questions that you can use to formulate a stellar hypothesis. So, ensure you pick a research topic of interest to scrutinize the world’s phenomena, processes, and events.
Step #2: Do Initial Research
Carry out preliminary research and gather essential background information about your topic of choice.
The extent of the information you collect will depend on what you want to prove.
Your initial research can be complete with a few academic books or a simple Internet search for quick answers with relevant statistics.
Still, keep in mind that in this phase, it is too early to prove or disapprove of your hypothesis.
Step #3: Identify Your Variables
Now that you have a basic understanding of the topic, choose the dependent and independent variables.
Take note that independent variables are the ones you can’t control, so understand the limitations of your test before settling on a final hypothesis.
Step #4: Formulate Your Hypothesis
You can write your hypothesis as an ‘if – then’ expression . Presenting any hypothesis in this format is reliable since it describes the cause-and-effect you want to test.
For instance: If I study every day, then I will get good grades.
Step #5: Gather Relevant Data
Once you have identified your variables and formulated the hypothesis, you can start the experiment. Remember, the conclusion you make will be a proof or rebuttal of your initial assumption.
So, gather relevant information, whether for a simple or statistical hypothesis, because you need to back your statement.
Step #6: Record Your Findings
Finally, write down your conclusions in a research paper .
Outline in detail whether the test has proved or disproved your hypothesis.
Edit and proofread your work, using a plagiarism checker to ensure the authenticity of your text.
We hope that the above tips will be useful for you. Note that if you need to conduct business analysis, you can use the free templates we’ve prepared: SWOT , PESTLE , VRIO , SOAR , and Porter’s 5 Forces .
❓ Hypothesis Formulator FAQ
Updated: Oct 25th, 2023
- How to Write a Hypothesis in 6 Steps - Grammarly
- Forming a Good Hypothesis for Scientific Research
- The Hypothesis in Science Writing
- Scientific Method: Step 3: HYPOTHESIS - Subject Guides
- Hypothesis Template & Examples - Video & Lesson Transcript
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Job Openings
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- IvyPanda Shop
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
Use our hypothesis maker whenever you need to formulate a hypothesis for your study. We offer a very simple tool where you just need to provide basic info about your variables, subjects, and predicted outcomes. The rest is on us. Get a perfect hypothesis in no time!
- Campus News
- Student News
- UK HealthCare
- UK Happenings
- Arts & Culture
- Professional News
UK project on bacteria-focused research selected for Hypothesis Fund seed grant

LEXINGTON, Ky. (June 14, 2024) — A researcher at the University of Kentucky has been selected to receive a seed grant from the Hypothesis Fund for the “boldness of her science and potential long-term impact of her work.”
The Hypothesis Fund supports early-stage, innovative research focused on addressing systemic risks to human and planetary health. They offer seed grants for novel, very early-stage research projects, with the goal of sparking new basic science discoveries.
Natalia Korotkova, Ph.D., is an assistant professor in the Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Molecular Genetics in the College of Medicine . As a microbiologist and biochemist, her work focuses on understanding cell biology of bacteria.
Her project titled “Functional significance of extracytoplasmic intrinsically disordered regions in streptococci” was selected for a seed grant by a Hypothesis Fund Scout — outstanding scientists who identify other scientists to fund.
“I am grateful to the Hypothesis Fund Scout, Dr. Mougous, who saw the potential of my work and pushed for this seed grant,” said Korotkova. “I’m looking forward to what we’ll discover through this project and the impact it could have on Kentucky and our country.”
Korotkova will study the roles and activities of specific parts of membrane proteins in streptococcal bacteria to determine how those contribute to the bacteria’s function, including interacting with a host or adapting to environments.
Korotkova was nominated by Joseph Mougous, Ph.D., a professor of microbiology at the University of Washington.
“Dr. Korotkova is seamlessly combining bacterial genetics and physiology with in-depth biochemistry to understand the regulatory mechanisms of intrinsically disordered regions (IDR) in bacterial proteins — all while keeping an eye on the human pathogenic side of the organisms,” said Mougous. “Her project could reveal bacterial IDRs as a fruitful and important area of investigation, with especially broad ramifications on the field of microbiology.”
As the state’s flagship, land-grant institution, the University of Kentucky exists to advance the Commonwealth. We do that by preparing the next generation of leaders — placing students at the heart of everything we do — and transforming the lives of Kentuckians through education, research and creative work, service and health care. We pride ourselves on being a catalyst for breakthroughs and a force for healing, a place where ingenuity unfolds. It's all made possible by our people — visionaries, disruptors and pioneers — who make up 200 academic programs, a $476.5 million research and development enterprise and a world-class medical center, all on one campus.
In 2022, UK was ranked by Forbes as one of the “Best Employers for New Grads” and named a “Diversity Champion” by INSIGHT into Diversity, a testament to our commitment to advance Kentucky and create a community of belonging for everyone. While our mission looks different in many ways than it did in 1865, the vision of service to our Commonwealth and the world remains the same. We are the University for Kentucky.
Latest Stories
‘great teacher’ eric weber captures students’ attention by exploring their interests, international postdoc continues research into space exploration at uk, new #ichampionhealth initiative targets improving health in lexington, monument honors the work of lexington abolitionists lewis and harriet hayden, uk law students continue work to solve cold cases with crrj-ky.

COMMENTS
6. Write a null hypothesis. If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing, you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0, while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a.
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
3. Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
This statement is based on background research and current knowledge.8,9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable.3,11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored.4.
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
A research hypothesis helps test theories. A hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method by providing a basis for testing existing theories. For example, a hypothesis might test the predictive power of a psychological theory on human behavior. It serves as a great platform for investigation activities.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation ('x affects y because …'). A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses.
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing: State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1 ). Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis. Perform an appropriate statistical test. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Present the findings in your results ...
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions. Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis: Predicts the relationship and outcome.
An empirical hypothesis is the opposite of a logical hypothesis. It is a hypothesis that is currently being tested using scientific analysis. We can also call this a 'working hypothesis'. We can to separate research into two types: theoretical and empirical. Theoretical research relies on logic and thought experiments.
A research hypothesis predicts an answer to the research question based on existing theoretical knowledge or experimental data. Some studies may have multiple hypothesis statements depending on the research question(s). A research hypothesis must be based on formulas, facts, and theories. It should be testable by data analysis, observations ...
A research hypothesis is an educated, clear, specific and falsifiable prediction of the possible outcomes of scientific observation. A hypothesis can be considered as the starting point of research, as any research without it is aimless. For a hypothesis to be complete, it should contain three main elements, i.e., two or more variables, a ...
Formulate the Hypotheses: Write your research hypotheses as a null hypothesis (H 0) and an alternative hypothesis (H A).; Data Collection: Gather data specifically aimed at testing the hypothesis.; Conduct A Test: Use a suitable statistical test to analyze your data.; Make a Decision: Based on the statistical test results, decide whether to reject the null hypothesis or fail to reject it.
The steps to write a research hypothesis are: 1. Stating the problem: Ensure that the hypothesis defines the research problem. 2. Writing a hypothesis as an 'if-then' statement: Include the action and the expected outcome of your study by following a 'if-then' structure. 3.
A research hypothesis is a mathematical way of stating a research question. A research hypothesis names the groups (we'll start with a sample and a population), what was measured, and which we think will have a higher mean. The last one gives the research hypothesis a direction. In other words, a research hypothesis should include:
Research hypothesis. The primary research question should be driven by the hypothesis rather than the data. 1, 2 That is, the research question and hypothesis should be developed before the start of the study. This sounds intuitive; however, if we take, for example, a database of information, it is potentially possible to perform multiple ...
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation ("x affects y because …"). A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses.
A Hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between two or more variables in a research study. Hypotheses are used in studies that aim to test cause-and-effect relationships between variables. A hypothesis is a tentative explanation for an observed phenomenon, and it is often derived from existing theory or previous research.
A hypothesis is a statement of the researcher's expectation or prediction about relationship among study variables. The research process begins and ends with the hypothesis. It is core to the ...
Research Hypothesis Vs Null Hypothesis. The difference between Research Hypothesis Vs Null Hypothesis is as follows: Research Hypothesis. A Research Hypothesis is a tentative statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. It is based on a theoretical or conceptual framework and is typically tested through empirical research.
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
In a nutshell, a hypothesis directs and organizes the research methods you will use, forming a large section of research paper writing. Hypothesis vs. Theory. A hypothesis is a realistic expectation that researchers make before any investigation. It is formulated and tested to prove whether the statement is true.
This is the ultraterrestrial hypothesis, which includes as a subset the "cryptoterrestrial" hypothesis, namely the notion that UAP may reflect activities of intelligent beings concealed in stealth ...
LEXINGTON, Ky. (June 14, 2024) — A researcher at the University of Kentucky has been selected to receive a seed grant from the Hypothesis Fund for the "boldness of her science and potential long-term impact of her work." The Hypothesis Fund supports early-stage, innovative research focused on addressing systemic risks to human and planetary health.
A common low-calorie sweetener called xylitol, found in gum, candy, toothpaste and more, may cause clots that can lead to heart attack and stroke, a new study found.